Page 68 - DMGT546_INTERNATIONAL_TRADE_PROCEDURE_AND_DOCUMENTATION
P. 68
Unit 3: EXIM Strategies
3.5.4 A Multi-country Strategy or a Global Strategy Notes
A multi-country strategy is appropriate for industries where multi-country competition
dominates and local responsiveness is essential. A global strategy works best in markets that
are globally competitive or beginning to globalize. A global strategy is one where the company’s
approach is mostly the same in all countries. Although minor country to country differences in
strategy do exist to accommodate specific competitive conditions in host countries, the company’s
fundamental competitive theme (low-cost, differentiation, best-cost, or focused) remains the
same world wide. The question of which of these two strategies to pursue is the foremost
strategic issue firms face when they compete in international markets. The following table
provides a point-by-point comparison of multi-country versus global strategies:
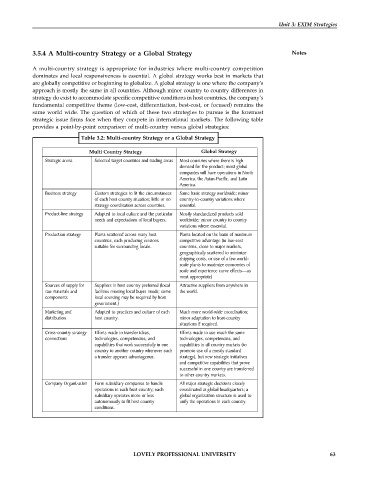
Table 3.2: Multi-country Strategy or a Global Strategy
Global Strategy
Multi Country Strategy d ddf
Strategic arena Selected target countries and trading areas Most countries where there is high
demand for the product; most global
companies will have operations in North
America, the Asian-Pacific, and Latin
America.
Business strategy Custom strategies to fit the circumstances Same basic strategy worldwide; minor
of each host country situation; little or no country-to-country variations where
strategy coordination across countries. essential.
Product-line strategy Adapted to local culture and the particular Mostly standardized products sold
needs and expectations of local buyers. worldwide; minor country to country
variations where essential.
Production strategy Plants scattered across many host Plants located on the basis of maximum
countries, each producing versions competitive advantage (in low-cost
suitable for surrounding locale. countries, close to major markets,
geographically scattered to minimize
shipping costs, or use of a few world-
scale plants to maximize economies of
scale and experience curve effects—as
most appropriate)
Sources of supply for Suppliers in host country preferred (local Attractive suppliers from anywhere in
raw materials and facilities meeting local buyer needs; some the world.
components local sourcing may be required by host
government.)
Marketing and Adapted to practices and culture of each Much more world-wide coordination;
distribution host country. minor adaptation to host-country
situations if required.
Cross-country strategy Efforts made to transfer ideas, Efforts made to use much the same
connections technologies, competencies, and technologies, competencies, and
capabilities that work successfully in one capabilities in all country markets (to
country to another country whenever such promote use of a mostly standard
a transfer appears advantageous. strategy), but new strategic initiatives
and competitive capabilities that prove
successful in one country are transferred
to other country markets.
Company Organization Form subsidiary companies to handle All major strategic decisions closely
operations in each host country; each coordinated at global headquarters; a
subsidiary operates more or less global organization structure is used to
autonomously to fit host country unify the operations in each country.
conditions.
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 63