Page 163 - DCAP304_DCAP515_SOFTWARE_PROJECT_MANAGEMENT
P. 163
Unit 8: Network Planning Model
Latest Start Time (LS) and Latest Finish Time (LF) Notes
The latest start (LS) and latest finish (LF) times of an activity are the latest times at which the
activity can start or finish without causing a delay in the completion of the project. Knowing
these times is valuable for the project manager, who must make decisions on resource scheduling
that can affect completion dates. The steps are as follows:
The window of time between the ES and LF of an activity is the window within which the
resource for the work must be scheduled or the project completion date will be delayed.
To calculate these times, you work backward in the network diagram. First set the LF time
of the last activity on the network to its calculated EF time. Its LS is calculated as [(LF –
Duration) + One time unit]. Again, you add the one time unit to adjust for the start and
finish of an activity within the same day.
The LF time of all immediate predecessor activities is determined by the minimum of the
LS, minus one time unit, times of all activities for which it is the predecessor.
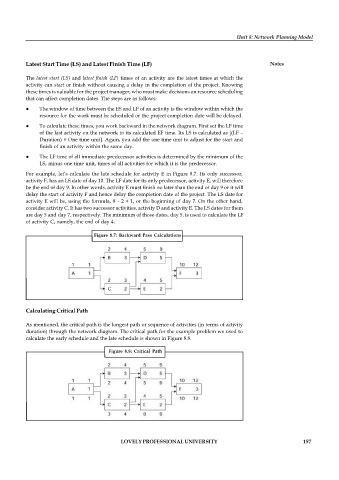
For example, let’s calculate the late schedule for activity E in Figure 8.7. Its only successor,
activity F, has an LS date of day 10. The LF date for its only predecessor, activity E, will therefore
be the end of day 9. In other words, activity E must finish no later than the end of day 9 or it will
delay the start of activity F and hence delay the completion date of the project. The LS date for
activity E will be, using the formula, 9 – 2 + 1, or the beginning of day 7. On the other hand,
consider activity C. It has two successor activities, activity D and activity E. The LS dates for them
are day 5 and day 7, respectively. The minimum of those dates, day 5, is used to calculate the LF
of activity C, namely, the end of day 4.
Figure 8.7: Backward Pass Calculations
Calculating Critical Path
As mentioned, the critical path is the longest path or sequence of activities (in terms of activity
duration) through the network diagram. The critical path for the example problem we used to
calculate the early schedule and the late schedule is shown in Figure 8.8.
Figure 8.8: Critical Path
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 157