Page 159 - DCAP304_DCAP515_SOFTWARE_PROJECT_MANAGEMENT
P. 159
Unit 8: Network Planning Model
Notes
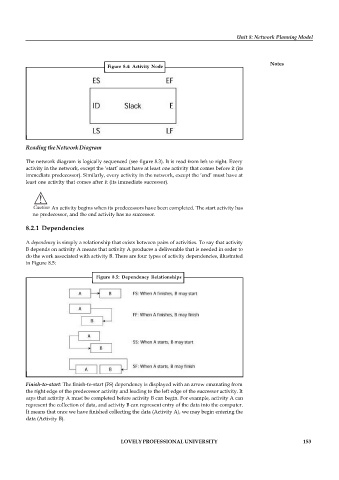
Figure 8.4: Activity Node
Reading the Network Diagram
The network diagram is logically sequenced (see figure 8.3). It is read from left to right. Every
activity in the network, except the ‘start’ must have at least one activity that comes before it (its
immediate predecessor). Similarly, every activity in the network, except the ‘end’ must have at
least one activity that comes after it (its immediate successor).
!
Caution An activity begins when its predecessors have been completed. The start activity has
no predecessor, and the end activity has no successor.
8.2.1 Dependencies
A dependency is simply a relationship that exists between pairs of activities. To say that activity
B depends on activity A means that activity A produces a deliverable that is needed in order to
do the work associated with activity B. There are four types of activity dependencies, illustrated
in Figure 8.5:
Figure 8.5: Dependency Relationships
Finish-to-start: The finish-to-start (FS) dependency is displayed with an arrow emanating from
the right edge of the predecessor activity and leading to the left edge of the successor activity. It
says that activity A must be completed before activity B can begin. For example, activity A can
represent the collection of data, and activity B can represent entry of the data into the computer.
It means that once we have finished collecting the data (Activity A), we may begin entering the
data (Activity B).
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 153