Page 56 - DCOM303_DMGT504_OPERATION_RESEARCH
P. 56
Unit 3: Linear Programming Problem – Simplex Method
Therefore, Z = C X Notes
B B
= 0 + 0 + 0
= 0
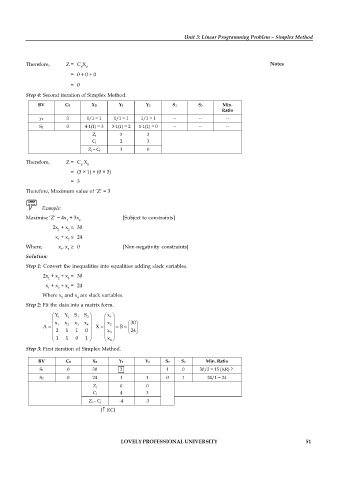
Step 4: Second iteration of Simplex Method.
BV CB XB Y1 Y2 S1 S2 Min.
Ratio
y2 3 1/1 = 1 1/1 = 1 1/1 = 1 -- -- --
S2 0 4-1(1) = 3 3-1(1) = 2 1-1(1) = 0 -- -- --
Zj 3 3
Cj 2 3
Zj – Cj 1 0
Therefore, Z = C X
B B
= (3 × 1) + (0 × 3)
= 3
Therefore, Maximum value of ‘Z’ = 3
Example:
Maximise ‘Z’ = 4x + 3x [Subject to constraints]
1 2
2x + x 30
1 2
x + x 24
1 2
Where, x , x 0 [Non-negativity constraints]
1 2
Solution:
Step 1: Convert the inequalities into equalities adding slack variables.
2x + x + x = 30
1 2 3
x + x + x = 24
1 2 4
Where x and x are slack variables.
3 4
Step 2: Fit the data into a matrix form.
Y 1 Y 2 S 1 S 2 x 1
x x x x x 30
A 1 2 3 4 X 2 B
2 1 1 0 x 24
3
1 1 0 1 x 4
Step 3: First iteration of Simplex Method.
BV CB XB Y1 Y2 S1 S2 Min. Ratio
S1 0 30 2 1 0 30/2 = 15 (KR) ?
S2 0 24 1 1 0 1 24/1 = 24
Zj 0 0
Cj 4 3
Zj – Cj -4 -3
( KC)
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 51