Page 98 - DCOM303_DMGT504_OPERATION_RESEARCH
P. 98
Unit 4: Linear Programming – Duality
Notes
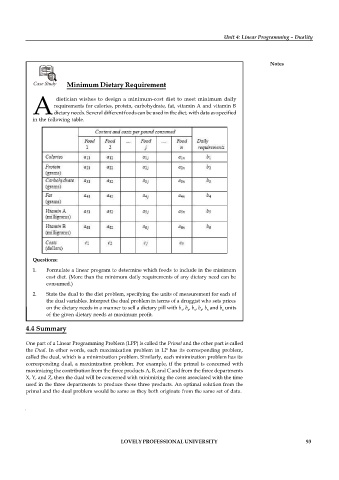
Case Study Minimum Dietary Requirement
dietician wishes to design a minimum-cost diet to meet minimum daily
requirements for calories, protein, carbohydrate, fat, vitamin A and vitamin B
A dietary needs. Several different foods can be used in the diet, with data as specified
in the following table.
Questions:
1. Formulate a linear program to determine which foods to include in the minimum
cost diet. (More than the minimum daily requirements of any dietary need can be
consumed.)
2. State the dual to the diet problem, specifying the units of measurement for each of
the dual variables. Interpret the dual problem in terms of a druggist who sets prices
on the dietary needs in a manner to sell a dietary pill with b , b , b , b , b and b units
1 2 3 4 5 6
of the given dietary needs at maximum profit.
4.4 Summary
One part of a Linear Programming Problem (LPP) is called the Primal and the other part is called
the Dual. In other words, each maximization problem in LP has its corresponding problem,
called the dual, which is a minimization problem. Similarly, each minimization problem has its
corresponding dual, a maximization problem. For example, if the primal is concerned with
maximizing the contribution from the three products A, B, and C and from the three departments
X, Y, and Z, then the dual will be concerned with minimizing the costs associated with the time
used in the three departments to produce those three products. An optimal solution from the
primal and the dual problem would be same as they both originate from the same set of data.
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 93