Page 109 - DMGT505_MANAGEMENT_INFORMATION_SYSTEM
P. 109
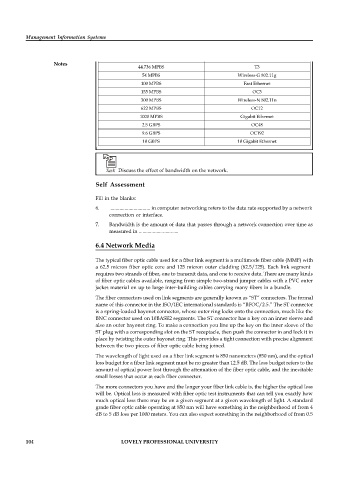
Bandwidth Device
56 KBPS Modem/Dial-up
Management Information Systems
1.5 MBPS ADSL Lite
1.544 MBPS T1
10 MPBS Wireless 802.11b
Notes
44.736 MPBS T3
54 MPBS Wireless-G 802.11g
100 MPBS Fast Ethernet
155 MPBS OC3
300 MPBS Wireless-N 802.11n
622 MPBS OC12
1000 MPBS Gigabit Ethernet
2.5 GBPS OC48
9.6 GBPS OC192
10 GBPS 10 Gigabit Ethernet
Task Discuss the effect of bandwidth on the network.
Self Assessment
Fill in the blanks:
6. ............................... in computer networking refers to the data rate supported by a network
connection or interface.
7. Bandwidth is the amount of data that passes through a network connection over time as
measured in ...............................
6.4 Network Media
The typical fiber optic cable used for a fiber link segment is a multimode fiber cable (MMF) with
a 62.5 micron fiber optic core and 125 micron outer cladding (62.5/125). Each link segment
requires two strands of fiber, one to transmit data, and one to receive data. There are many kinds
of fiber optic cables available, ranging from simple two-strand jumper cables with a PVC outer
jacket material on up to large inter-building cables carrying many fibers in a bundle.
The fiber connectors used on link segments are generally known as “ST” connectors. The formal
name of this connector in the ISO/IEC international standards is “BFOC/2.5.” The ST connector
is a spring-loaded bayonet connector, whose outer ring locks onto the connection, much like the
BNC connector used on 10BASE2 segments. The ST connector has a key on an inner sleeve and
also an outer bayonet ring. To make a connection you line up the key on the inner sleeve of the
ST plug with a corresponding slot on the ST receptacle, then push the connector in and lock it in
place by twisting the outer bayonet ring. This provides a tight connection with precise alignment
between the two pieces of fiber optic cable being joined.
The wavelength of light used on a fiber link segment is 850 nanometers (850 nm), and the optical
loss budget for a fiber link segment must be no greater than 12.5 dB. The loss budget refers to the
amount of optical power lost through the attenuation of the fiber optic cable, and the inevitable
small losses that occur at each fiber connector.
The more connectors you have and the longer your fiber link cable is, the higher the optical loss
will be. Optical loss is measured with fiber optic test instruments that can tell you exactly how
much optical loss there may be on a given segment at a given wavelength of light. A standard
grade fiber optic cable operating at 850 nm will have something in the neighborhood of from 4
dB to 5 dB loss per 1000 meters. You can also expect something in the neighborhood of from 0.5
104 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY