Page 168 - DMGT505_MANAGEMENT_INFORMATION_SYSTEM
P. 168
Unit 8: Databases and Data Warehouses
Notes
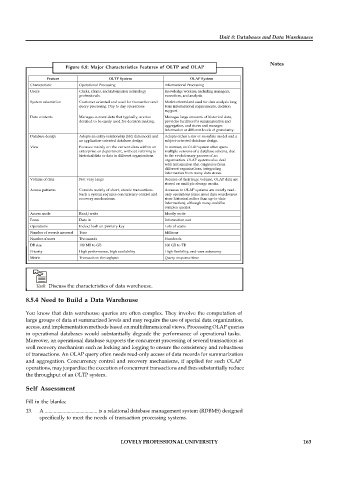
Figure 8.8: Major Characteristics Features of OLTP and OLAP
Feature OLTP System OLAP System
Characteristic Operational Processing Informational Processing
Users Clerks, clients, and information technology Knowledge workers, including managers,
professionals. executives, and analysts.
System orientation Customer oriented and used for transaction and Market-oriented and used for data analysis long
query processing Day to day operations term informational requirements, decision
support.
Data contents Manages current data that typically, are too Manages large amounts of historical data,
detailed to be easily used for decision making. provides facilities for summarisation and
aggregation, and stores and manages
information at different levels of granularity.
Database design Adopts an entity-relationship (ER) data model and Adopts either a star or snowflake model and a
an application-oriented database design subject-oriented database design.
View Focuses mainly on the current data within an In contrast, an OLAP system often spans
enterprise or department, without referring to multiple versions of a database schema, due
historical data or data in different organisations. to the evolutionary process of an
organisation. OLAP systems also deal
with information that originates from
different organisations, integrating
information from many data stores.
Volume of data Not very large Because of their huge volume, OLAP data are
stored on multiple storage media.
Access patterns Consists mainly of short, atomic transactions. Accesses to OLAP systems are mostly read-
Such a system requires concurrency control and only operations (since most data warehouses
recovery mechanisms. store historical rather than up-to-date
information), although many could be
complex queries.
Access mode Read/write Mostly write
Focus Data in Information out
Operations Index/hash on primary key Lots of scans
Number of records accessed Tens Millions
Number of users Thousands Hundreds
DB size 100 MB to GB 100 GB to TB
Priority High performance, high availability High flexibility, end-user autonomy
Metric Transaction throughput Query response time
Task Discuss the characteristics of data warehouse.
8.5.4 Need to Build a Data Warehouse
You know that data warehouse queries are often complex. They involve the computation of
large groups of data at summarized levels and may require the use of special data organization,
access, and implementation methods based on multidimensional views. Processing OLAP queries
in operational databases would substantially degrade the performance of operational tasks.
Moreover, an operational database supports the concurrent processing of several transactions as
well recovery mechanism such as locking and logging to ensure the consistency and robustness
of transactions. An OLAP query often needs read-only access of data records for summarization
and aggregation. Concurrency control and recovery mechanisms, if applied for such OLAP
operations, may jeopardize the execution of concurrent transactions and thus substantially reduce
the throughput of an OLTP system.
Self Assessment
Fill in the blanks:
13. A ......................................... is a relational database management system (RDBMS) designed
specifically to meet the needs of transaction processing systems.
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 163