Page 84 - DMGT505_MANAGEMENT_INFORMATION_SYSTEM
P. 84
Unit 5: Business Hardware Software and IT Infrastructure
Notes
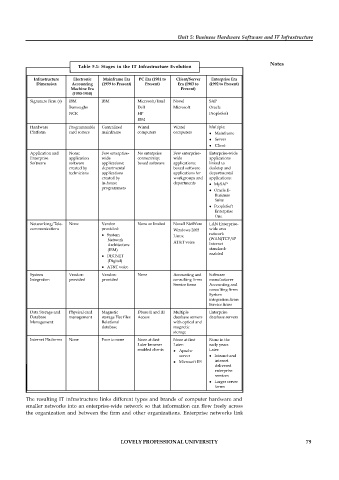
Table 5.1: Stages in the IT Infrastructure Evolution
Infrastructure Electronic Mainframe Era PC Era (1981 to Client/Server Enterprise Era
Dimension Accounting (1959 to Present) Present) Era (1983 to (1992 to Present)
Machine Era Present)
(1930-1950)
Signature Firm (s) IBM IBM Microsoft/Intel Novel SAP
Burroughs Dell Microsoft Oracle
NCR HP PeopleSoft
IBM
Hardware Programmable Centralized Wintel Wintel Multiple:
Platform card sorters mainframe computers computers Mainframe
Server
Client
Application and None; Few enterprise- No enterprise Few enterprise- Enterprise-wide
Enterprise application wide connectivity; wide applications
Software software applications; boxed software applications; linked to
created by departmental boxed software desktop and
technicians applications applications for departmental
created by workgroups and applications:
in-house departments MySAP
programmers
Oracle E-
Business
Suite
PeopleSoft
Enterprise
One
Networking/Tele- None Vendor None or limited Novell NetWare LAN Enterprise-
communications provided: Windows 2003 wide area
System Linux network
Network AT&T voice (WAN)TCP/IP
Architecture Internet
(IBM) standard-
enabled
DECNET
(Digital)
AT&T voice
System Vendor- Vendor- None Accounting and Software
Integration provided provided consulting firms manufacturer
Service firms Accounting and
consulting firms
System
integration firms
Service firms
Data Storage and Physical card Magnetic Dbase II and III Multiple Enterprise
Database management storage Flat files Access database servers database servers
Management Relational with optical and
database magnetic
storage
Internet Platforms None Poor to none None at first None at first None in the
Later browser Later: early years
enabled clients Apache Later:
server Intranet and
Microsoft IIS internet
delivered
enterprise
services
Larger server
farms
The resulting IT infrastructure links different types and brands of computer hardware and
smaller networks into an enterprise-wide network so that information can flow freely across
the organization and between the firm and other organizations. Enterprise networks link
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 79