Page 14 - DMGT510_SERVICES_MARKETING
P. 14
Unit 1: Introduction to Services Marketing
Notes
Example: An airline is primarily offering the passenger transportation service. However
airlines also offer food and entertainment on board.
The primary item, in this case, still remains transportation and food, entertainment, etc., remain
secondary. Lastly, it is the pure service where the offer is only a service.
Example: Telecommunication, psychotherapy, health club, etc.
Self Assessment
Fill in the blanks:
8. Teaching is a ................... service.
9. Bathing soap is a pure tangible ...................
10. Clothes come under the category of ................... goods.
11. Manicure and Pedicure are types of ................... goods.
1.4 Classification of Services
Ever since marketing researchers started defining services, they also proposed their classification.
The first one was proposed as early as 1964 and the last, as late as 1989. Summary of these
classifications has been given in Tables 1.3.
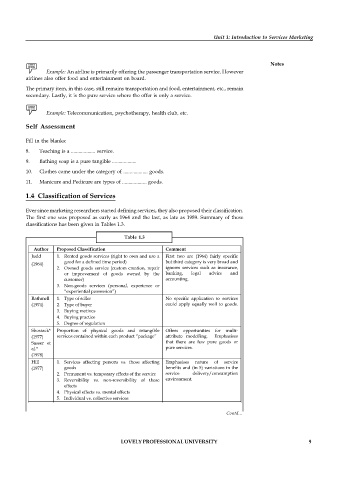
Table 1.3
Author Proposed Classification Comment
Judd 1. Rented goods services (right to own and use a First two are (1964) fairly specific
(1964) good for a defined time period) but third category is very broad and
2. Owned goods service (custom creation, repair ignores services such as insurance,
or improvement of goods owned by the banking, legal advice and
customer) accounting.
3. Non-goods services (personal, experience or
“experiential possession”)
Rathmell 1. Type of seller No specific application to services
(1974) 2. Type of buyer could apply equally well to goods.
3. Buying motives
4. Buying practice
5. Degree of regulation
Shostack* Proportion of physical goods and intangible Offers opportunities for multi-
(1977) services contained within each product “package” attribute modelling. Emphasises
Sasser et that there are few pure goods or
al.* pure services.
(1978)
Hill 1. Services affecting persons vs. those affecting Emphasises nature of service
(1977) goods benefits and (in 5) variations in the
2. Permanent vs. temporary effects of the service service delivery/consumption
3. Reversibility vs. non-reversibility of these environment.
effects
4. Physical effects vs. mental effects
5. Individual vs. collective services
Contd...
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 9