Page 18 - DMGT513_DERIVATIVES_AND_RISK_MANAGEMENT
P. 18
Unit 2: Evolution of Derivatives in India
various commodities were allowed to trade on exchanges. For example, now cotton and oil Notes
futures trade in Mumbai, soyabean futures trade in Bhopal, pepper futures in Kochi, coffee
futures in Bangalore etc. In June 2000, the National Stock Exchange and the Bombay Stock
Exchange started trading in futures on Sensex and Nifty. Options trading on Sensex and Nifty
commenced in June 2001. Very soon thereafter, trading began on options and futures in 31
prominent stocks in the month of July and November respectively. Currently there are 41 stocks
trading on NSE Derivative and the list keeps growing.
!
Caution A primary motivation for pre-arranging a buyer or seller for a stock of
commodities in early forward contracts was to lessen the possibility that large swings
would inhibit marketing the commodity after a harvest.
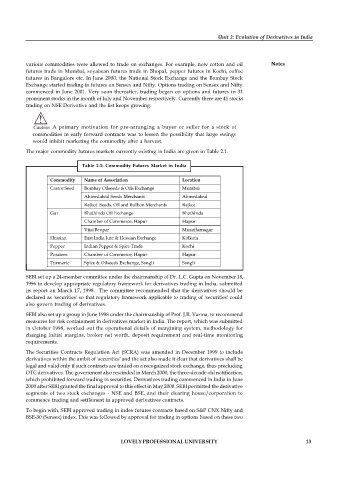
The major commodity futures markets currently existing in India are given in Table 2.1.
Table 2.1: Commodity Futures Market in India
Commodity Name of Association Location
Castor Seed Bombay Oilseeds & Oils Exchange Mumbai
Ahmedabad Seeds Merchants Ahmedabad
Rajkot Seeds, Oil and Bullion Merchants Rajkot
Gur Bhathinda Oil Exchange Bhathinda
Chamber of Commerce, Hapur Hapur
Vijai Beopar Muzaffarnagar
Hessian East India Jute & Hessian Exchange Kolkata
Pepper Indian Pepper & Spice Trade Kochi
Potatoes Chamber of Commerce, Hapur Hapur
Turmeric Spice & Oilseeds Exchange, Sangli Sangli
SEBI set up a 24-member committee under the chairmanship of Dr. L.C. Gupta on November 18,
1996 to develop appropriate regulatory framework for derivatives trading in India, submitted
its report on March 17, 1998. The committee recommended that the derivatives should be
declared as 'securities' so that regulatory framework applicable to trading of 'securities' could
also govern trading of derivatives.
SEBI also set up a group in June 1998 under the chairmanship of Prof. J.R. Varma, to recommend
measures for risk containment in derivatives market in India. The report, which was submitted
in October 1998, worked out the operational details of margining system, methodology for
charging initial margins, broker net worth, deposit requirement and real-time monitoring
requirements.
The Securities Contracts Regulation Act (SCRA) was amended in December 1999 to include
derivatives within the ambit of 'securities' and the act also made it clear that derivatives shall be
legal and valid only if such contracts are traded on a recognized stock exchange, thus precluding
OTC derivatives. The government also rescinded in March 2000, the three-decade old notification,
which prohibited forward trading in securities. Derivatives trading commenced in India in June
2000 after SEBI granted the final approval to this effect in May 2000. SEBI permitted the derivative
segments of two stock exchanges - NSE and BSE, and their clearing house/corporation to
commence trading and settlement in approved derivatives contracts.
To begin with, SEBI approved trading in index futures contracts based on S&P CNX Nifty and
BSE-30 (Sensex) index. This was followed by approval for trading in options based on these two
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 13