Page 98 - DMGT513_DERIVATIVES_AND_RISK_MANAGEMENT
P. 98
Unit 7: Option Strategies and Pay-offs
Notes
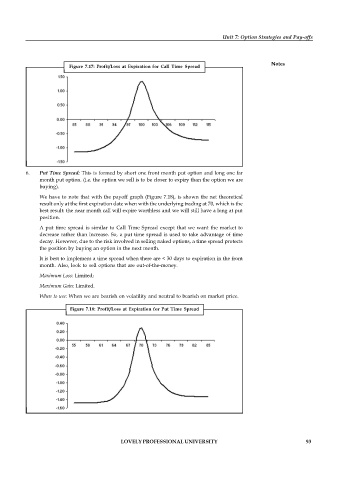
Figure 7.17: Profit/Loss at Expiration for Call Time Spread
6. Put Time Spread: This is formed by short one front month put option and long one far
month put option. (i.e. the option we sell is to be closer to expiry than the option we are
buying).
We have to note that with the payoff graph (Figure 7.18), is shown the net theoretical
result only at the first expiration date when with the underlying trading at 70, which is the
best result: the near month call will expire worthless and we will still have a long at put
position.
A put time spread is similar to Call Time Spread except that we want the market to
decrease rather than increase. So, a put time spread is used to take advantage of time
decay. However, due to the risk involved in selling naked options, a time spread protects
the position by buying an option in the next month.
It is best to implement a time spread when there are < 30 days to expiration in the front
month. Also, look to sell options that are out-of-the-money.
Maximum Loss: Limited;
Maximum Gain: Limited.
When to use: When we are bearish on volatility and neutral to bearish on market price.
Figure 7.18: Profit/Loss at Expiration for Put Time Spread
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 93