Page 57 - DMGT515_PERSONAL_FINANCIAL_PLANNING
P. 57
Personal Financial Planning
Notes Financial advisors generally classify investors into the following categories based on investor
risk:
Conservative
Moderately conservative
Aggressive
Very aggressive
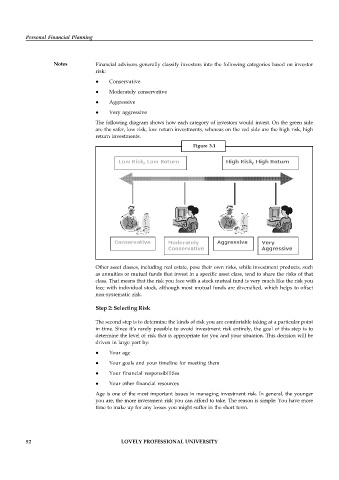
The following diagram shows how each category of investors would invest. On the green side
are the safer, low risk, low return investments, whereas on the red side are the high risk, high
return investments.
Figure 3.1
Other asset classes, including real estate, pose their own risks, while investment products, such
as annuities or mutual funds that invest in a specific asset class, tend to share the risks of that
class. That means that the risk you face with a stock mutual fund is very much like the risk you
face with individual stock, although most mutual funds are diversified, which helps to offset
non-systematic risk.
Step 2: Selecting Risk
The second step is to determine the kinds of risk you are comfortable taking at a particular point
in time. Since it’s rarely possible to avoid investment risk entirely, the goal of this step is to
determine the level of risk that is appropriate for you and your situation. This decision will be
driven in large part by:
Your age
Your goals and your timeline for meeting them
Your financial responsibilities
Your other financial resources
Age is one of the most important issues in managing investment risk. In general, the younger
you are, the more investment risk you can afford to take. The reason is simple: You have more
time to make up for any losses you might suffer in the short term.
52 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY