Page 53 - DMGT515_PERSONAL_FINANCIAL_PLANNING
P. 53
Personal Financial Planning
Notes 4. Skewness (Sk): Skewness tells us about the symmetry of the data. Sometimes, a given data
of two distributions may produce same mean and the same standard deviation. But the
data may differ in terms of the shape of distribution. If a given data are not symmetrical,
it is called asymmetrical or skewed. Higher skewness implies higher dispersion. In
skewness, there are two possibilities, of data being: (i) positively skewed and; (ii) negatively
skewed. Positive skewness implies that there is less likelihood of returns being lower
than the mean. Whereas, negative skewness implies higher deviations from the mean.
Therefore, positive skewness is considered less risky.
5. Probability Distribution: Probability distribution is a measure of someone’s opinion
about the likelihood that an event will occur. In other words, a probability distribution is
a statement of the different potential outcomes for an uncertain variable together with the
probability of each potential outcome. Typically, probability distributions of returns are
estimated using actual historical data. By studying the behavior of stock returns over the
recent past, it is possible to come up with a subjective probability assessment for future
returns. While assessing risks and returns related to an investment, the expected return
from an investment is taken as the average of return from the investment and is calculated
as the probability weighted sum of all potential returns. Thus:
E(R)=S [P(r) × r]
Where:
E (R) = Expected return
P (r) = Probability of a particular value of return
r = return
S = sum of all possible outcomes
As per the above equation, each potential return be multiplied by its probability occurrence
and then all these products are to be added together.
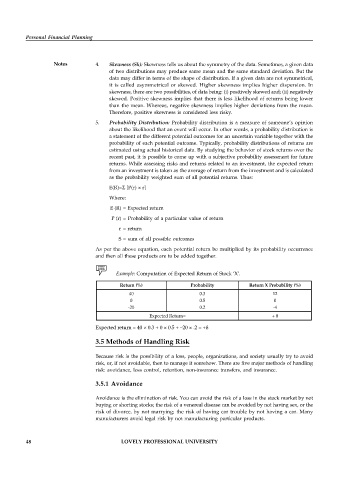
Example: Computation of Expected Return of Stock ‘X’.
Return (%) Probability Return X Probability (%)
40 0.3 12
0 0.5 0
-20 0.2 -4
Expected Return= + 8
Expected return = 40 × 0.3 + 0 × 0.5 + –20 × .2 = +8
3.5 Methods of Handling Risk
Because risk is the possibility of a loss, people, organizations, and society usually try to avoid
risk, or, if not avoidable, then to manage it somehow. There are five major methods of handling
risk: avoidance, loss control, retention, non-insurance transfers, and insurance.
3.5.1 Avoidance
Avoidance is the elimination of risk. You can avoid the risk of a loss in the stock market by not
buying or shorting stocks; the risk of a venereal disease can be avoided by not having sex, or the
risk of divorce, by not marrying; the risk of having car trouble by not having a car. Many
manufacturers avoid legal risk by not manufacturing particular products.
48 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY