Page 321 - DMGT523_LOGISTICS_AND_SUPPLY_CHAIN_MANAGEMENT
P. 321
Logistics and Supply Chain Management
Notes
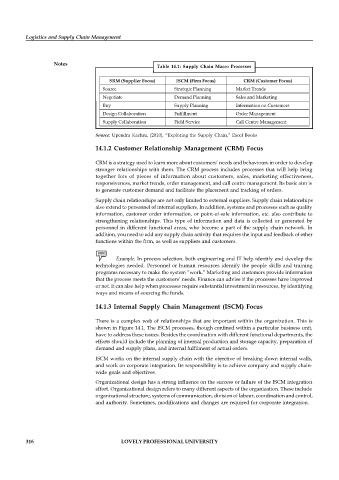
Table 14.1: Supply Chain Macro Processes
SRM (Supplier Focus) ISCM (Firm Focus) CRM (Customer Focus)
Source Strategic Planning Market Trends
Negotiate Demand Planning Sales and Marketing
Buy Supply Planning Information on Customers
Design Collaboration Fulfillment Order Management
Supply Collaboration Field Service Call Centre Management
Source: Upendra Kachru, (2010), “Exploring the Supply Chain,” Excel Books
14.1.2 Customer Relationship Management (CRM) Focus
CRM is a strategy used to learn more about customers’ needs and behaviours in order to develop
stronger relationships with them. The CRM process includes processes that will help bring
together lots of pieces of information about customers, sales, marketing effectiveness,
responsiveness, market trends, order management, and call centre management. Its basic aim is
to generate customer demand and facilitate the placement and tracking of orders.
Supply chain relationships are not only limited to external suppliers. Supply chain relationships
also extend to personnel of internal suppliers. In addition, systems and processes such as quality
information, customer order information, or point-of-sale information, etc. also contribute to
strengthening relationships. This type of information and data is collected or generated by
personnel in different functional areas, who become a part of the supply chain network. In
addition, you need to add any supply chain activity that requires the input and feedback of other
functions within the firm, as well as suppliers and customers.
Example: In process selection, both engineering and IT help identify and develop the
technologies needed. Personnel or human resources identify the people skills and training
programs necessary to make the system “work.” Marketing and customers provide information
that the process meets the customers’ needs. Finance can advise if the processes have improved
or not. It can also help when processes require substantial investment in resources, by identifying
ways and means of sourcing the funds.
14.1.3 Internal Supply Chain Management (ISCM) Focus
There is a complex web of relationships that are important within the organization. This is
shown in Figure 14.1. The ISCM processes, though confined within a particular business unit,
have to address these issues. Besides the coordination with different functional departments, the
efforts should include the planning of internal production and storage capacity, preparation of
demand and supply plans, and internal fulfilment of actual orders.
ISCM works on the internal supply chain with the objective of breaking down internal walls,
and work on corporate integration. Its responsibility is to achieve company and supply chain-
wide goals and objectives.
Organizational design has a strong influence on the success or failure of the ISCM integration
effort. Organizational design refers to many different aspects of the organization. These include
organizational structure, systems of communication, division of labour, coordination and control,
and authority. Sometimes, modifications and changes are required for corporate integration.
316 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY