Page 89 - DMGT523_LOGISTICS_AND_SUPPLY_CHAIN_MANAGEMENT
P. 89
Logistics and Supply Chain Management
Notes The need for collaborative forecasting arises due to increasing competition and the requirement
that manufacturers in a supply chain must synchronize operations to derive the benefits of
collaboration. Understocking as well as overstocking of inventory, both cause problems and
decrease a manufacturer’s competitiveness. Collaborative forecasting can help eliminate excess
inventory and at the same time, support the supply chain management initiative of the
participating companies. A generic model of CPFR system is shown as Figure 4.1.
Self Assessment
State whether the following statements are true or false:
6. CPFR is accepted as an extension of supply chain Philosophy and as a part of supply chain
management.
7. Supportive data, such as past sales trends were transferred in an iterative fashion.
8. Collaborative forecasting overcomes some of the inherent problems with modern
forecasting.
9. Collaborative forecasting can help eliminate excess inventory.
10. Collaborative forecasting involves the entire supply chain that participates in decisions
about demand.
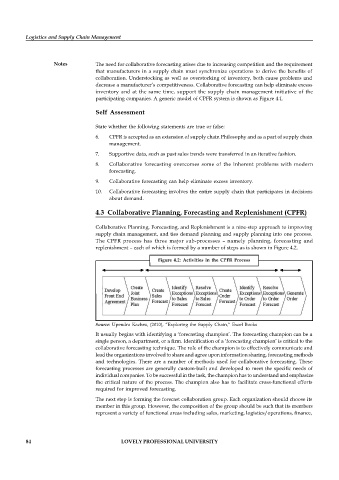
4.3 Collaborative Planning, Forecasting and Replenishment (CPFR)
Collaborative Planning, Forecasting, and Replenishment is a nine-step approach to improving
supply chain management, and ties demand planning and supply planning into one process.
The CPFR process has three major sub-processes – namely planning, forecasting and
replenishment – each of which is formed by a number of steps as is shown in Figure 4.2.
Figure 4.2: Activities in the CPFR Process
Source: Upendra Kachru, (2010), “Exploring the Supply Chain,” Excel Books
It usually begins with identifying a ‘forecasting champion’. The forecasting champion can be a
single person, a department, or a firm. Identification of a ‘forecasting champion’ is critical to the
collaborative forecasting technique. The role of the champion is to effectively communicate and
lead the organizations involved to share and agree upon information sharing, forecasting methods
and technologies. There are a number of methods used for collaborative forecasting. These
forecasting processes are generally custom-built and developed to meet the specific needs of
individual companies. To be successful in the task, the champion has to understand and emphasize
the critical nature of the process. The champion also has to facilitate cross-functional efforts
required for improved forecasting.
The next step is forming the forecast collaboration group. Each organization should choose its
member in this group. However, the composition of the group should be such that its members
represent a variety of functional areas including sales, marketing, logistics/operations, finance,
84 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY