Page 74 - DLIS108_INFORMATION_AND_COMMUNICATION_TECHNOLOGY_APPLICATIONS
P. 74
VED1
e\L-lovely-eng\comm8-1.pmd IInd 16-9-11 IIIrd 22-12-11 IVth 4-1-12
Unit 8: Programming Language: Types and Functions
8.3 Aspects of Programming Languages
Notes
Programming Languages includes following aspects:
• A paradigm is a coherent set of methods found useful for solving problems in a given prob-
lem domain.
• A paradigm is characterized by a principle; this supplies the basis for a limited number of con-
cepts, which allow infinitely many methods to be invented, which in their turn help the pro-
grammer in solving the problem at hand.
• Grammar describes the form of programs; semantics is attached to grammatical notions.
• Syntactic structure define the program text, the grammar defines a parsing, which recovers the
notions and therewith the semantics.
• Abstraction is to ignore irrelevant detail in a safe way. This is done by hiding information
behind an interface.
8.4 Hierarchy of Programming Languages
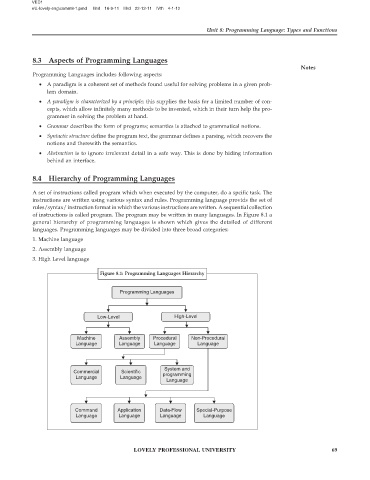
A set of instructions called program which when executed by the computer, do a spcific task. The
instructions are written using various syntax and rules. Programming language provids the set of
rules/syntax/ instruction format in which the various instructions are written. A sequential collection
of instructions is called program. The program may be written in many languages. In Figure 8.1 a
general hierarchy of programming languages is shown which gives the detailed of different
languages. Programming languages may be divided into three broad categories:
1. Machine language
2. Assembly language
3. High Level language
Figure 8.1: Programming Languages Hierarchy
Programming Languages
Low-Level High-Level
Machine Assembly Procedural Non-Procedural
Language Language Language Language
System and
Commercial Scientific
Language Language programming
Language
Command Application Data-Flow Special-Purpose
Language Language Language Language
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 69