Page 13 - DLIS002_KNOWLEDGE ORGANIZATION CLASSIFICATION AND CATALOGUING THEORY
P. 13
Knowledge Organization: Classification and Cataloguing Theory
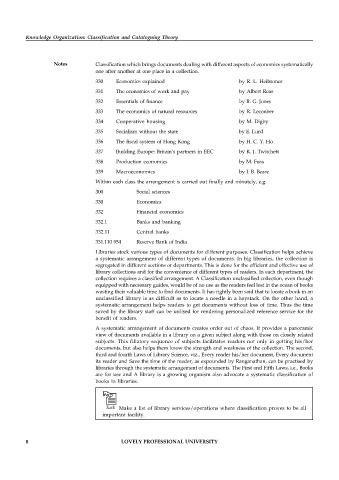
Notes Classification which brings documents dealing with different aspects of economics systematically
one after another at one place in a collection.
330 Economics explained by R. L. Heibroner
331 The economics of work and pay by Albert Reas
332 Essentials of finance by R. G. Jones
333 The economics of natural resources by R. Leconber
334 Cooperative housing by M. Digby
335 Socialism without the state by E. Lurd
336 The fiscal system of Hong Kong by H. C. Y. Ho
337 Building Europe: Britain’s partners in EEC by K. J. Twitchett
338 Production economics by M. Fuss
339 Macroeconomics by J. B. Beare
Within each class the arrangement is carried out finally and minutely, e.g.
300 Social sciences
330 Economics
332 Financial economics
332.1 Banks and banking
332.11 Central banks
331.110 954 Reserve Bank of India
Libraries stock various types of documents for different purposes. Classification helps achieve
a systematic arrangement of different types of documents. In big libraries, the collection is
segregated in different sections or departments. This is done for the efficient and effective use of
library collections and for the convenience of different types of readers. In each department, the
collection requires a classified arrangement. A Classification unclassified collection, even though
equipped with necessary guides, would be of no use as the readers feel lost in the ocean of books
wasting their valuable time to find documents. It has rightly been said that to locate a book in an
unclassified library is as difficult as to locate a needle in a haystack. On the other hand, a
systematic arrangement helps readers to get documents without loss of time. Thus the time
saved by the library staff can be utilised for rendering personalized reference service for the
benefit of readers.
A systematic arrangement of documents creates order out of chaos. It provides a panoramic
view of documents available in a library on a given subject along with those on closely related
subjects. This filiatory sequence of subjects facilitates readers not only in getting his/her
documents, but also helps them know the strength and weakness of the collection. The second,
third and fourth Laws of Library Science, viz., Every reader his/her document, Every document
its reader and Save the time of the reader, as expounded by Ranganathan, can be practised by
libraries through the systematic arrangement of documents. The First and Fifth Laws, i.e., Books
are for use and A library is a growing organism also advocate a systematic classification of
books in libraries.
Task Make a list of library services/operations where classification proves to be all
important facility.
8 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY