Page 72 - DCAP104_EXPOSURE_TO_COMPUTER_DISCPLINES
P. 72
Unit 4: Introduction of Networks
Advantages Notes
• Centralised user accounts, security and access controls simplify network administration.
• More powerful equipment means more efficient access network resources.
• Single password login, means access to all resources.
• Supports greater numbers of users, or networks where resources are heavily used.
Disadvantages
• More costly to install and maintain.
• Single point of failure, server goes down, the network goes down.
• Complex special-purpose software requires appointment of expert staff, increasing costs.
• Dedicated hardware and software increases costs.
4.3.2 Local Area Network
A local area network (LAN) is a network that connects computers and devices in a limited
geographical area such as home, school, computer laboratory, office building, or closely positioned
group of buildings. Each computer or device on the network is a node. Current wired LANs are
most likely to be based on Ethernet technology, although new standards like ITU-T G.hn also
provide a way to create a wired LAN using existing home wires (coaxial cables, phone lines and
power lines).
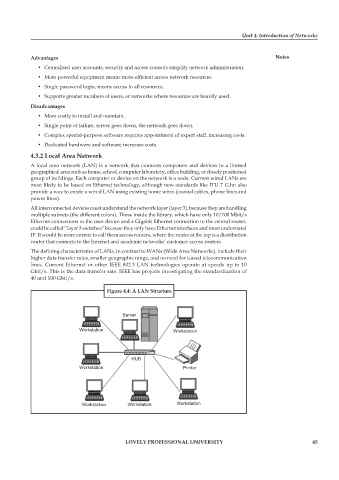
All interconnected devices must understand the network layer (layer 3), because they are handling
multiple subnets (the different colors). Those inside the library, which have only 10/100 Mbit/s
Ethernet connections to the user device and a Gigabit Ethernet connection to the central router,
could be called “layer 3 switches” because they only have Ethernet interfaces and must understand
IP. It would be more correct to call them access routers, where the router at the top is a distribution
router that connects to the Internet and academic networks’ customer access routers.
The defining characteristics of LANs, in contrast to WANs (Wide Area Networks), include their
higher data transfer rates, smaller geographic range, and no need for leased telecommunication
lines. Current Ethernet or other IEEE 802.3 LAN technologies operate at speeds up to 10
Gbit/s. This is the data transfer rate. IEEE has projects investigating the standardization of
40 and 100 Gbit/s.
Figure 4.4: A LAN Structure
Server
Workstation Workstation
HUB
Workstation Printer
Workstation Workstation Workstation
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 65