Page 230 - DCOM102_DMGT101_PRINCIPLES_AND_PRACTICES_OF_MANAGEMENT
P. 230
Principles and Practices of Management
Notes 1. Resistance: The individuals in the organisation may resist changing. They may
(a) Be anxious about the change.
(b) Feel they will lose control, or
(c) Be unable to cope, or
(d) Have a vested interest in the existing state of things.
2. Control: During the transition and afterwards, this formal structure may no longer be
effective. Managers may lose the ability to monitor performance and make needed
corrections.
3. Power: Changes disrupt the existing balance of power, and especially during the transition
state cause individuals to engage in political (power-seeking) behaviour.
Awareness of these problem areas enables managers to prepare themselves to implement change
successfully.
12.6.3 A Contingency Model of Analyzing Change
Kotter and Schlesinger have proposed a contingency framework for matching methods with
situations of organisations. There proposal is shown in Table 12.2 below:
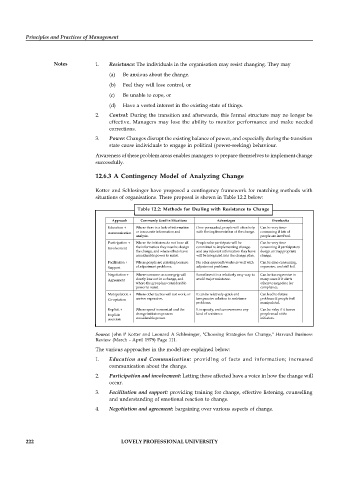
Table 12.2: Methods for Dealing with Resistance to Change
Source: John P Kotter and Leonard A Schlesinger, "Choosing Strategies for Change," Harvard Business
Review (March - April 1979) Page 111.
The various approaches in the model are explained below:
1. Education and Communication: providing of facts and information; increased
communication about the change.
2. Participation and involvement: Letting those affected have a voice in how the change will
occur.
3. Facilitation and support: providing training for change, effective listening, counselling
and understanding of emotional reaction to change.
4. Negotiation and agreement: bargaining over various aspects of change.
222 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY