Page 115 - DCOM203_DMGT204_QUANTITATIVE_TECHNIQUES_I
P. 115
Quantitative Techniques – I
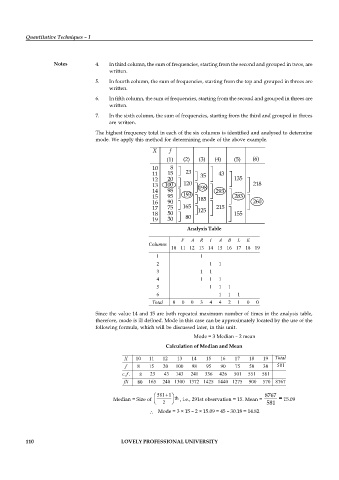
Notes 4. In third column, the sum of frequencies, starting from the second and grouped in twos, are
written.
5. In fourth column, the sum of frequencies, starting from the top and grouped in threes are
written.
6. In fifth column, the sum of frequencies, starting from the second and grouped in threes are
written.
7. In the sixth column, the sum of frequencies, starting from the third and grouped in threes
are written.
The highest frequency total in each of the six columns is identified and analysed to determine
mode. We apply this method for determining mode of the above example.
Analysis Table
V A R I A B L E
Columns
10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19
1 1
2 1 1
3 1 1
4 1 1 1
5 1 1 1
6 1 1 1
Total 0 0 0 3 4 4 2 1 0 0
Since the value 14 and 15 are both repeated maximum number of times in the analysis table,
therefore, mode is ill defined. Mode in this case can be approximately located by the use of the
following formula, which will be discussed later, in this unit.
Mode = 3 Median – 2 mean
Calculation of Median and Mean
X 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 Total
f 8 15 20 100 98 95 90 75 50 30 581
f
c . . 8 23 43 143 241 336 426 501 551 581
fX 80 165 240 1300 1372 1425 1440 1275 900 570 8767
581 1 8767
Median = Size of th , i.e., 291st observation = 15. Mean = = 15.09
2 581
Mode = 3 × 15 – 2 × 15.09 = 45 – 30.18 = 14.82
110 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY