Page 234 - DCOM203_DMGT204_QUANTITATIVE_TECHNIQUES_I
P. 234
Unit 11: Analysis of Time Series
Solution: Notes
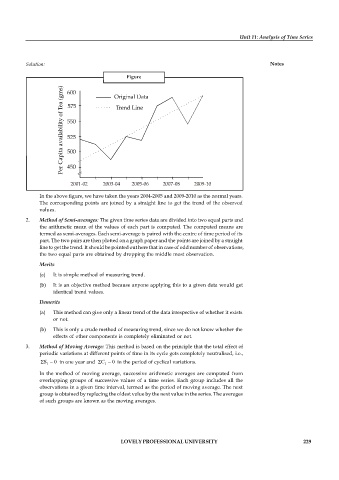
Figure
2001-02 2003-04 2005-06 2007-08 2009-10
In the above figure, we have taken the years 2004-2005 and 2009-2010 as the normal years.
The corresponding points are joined by a straight line to get the trend of the observed
values.
2. Method of Semi-averages: The given time series data are divided into two equal parts and
the arithmetic mean of the values of each part is computed. The computed means are
termed as semi-averages. Each semi-average is paired with the centre of time period of its
part. The two pairs are then plotted on a graph paper and the points are joined by a straight
line to get the trend. It should be pointed out here that in case of odd number of observations,
the two equal parts are obtained by dropping the middle most observation.
Merits
(a) It is simple method of measuring trend.
(b) It is an objective method because anyone applying this to a given data would get
identical trend values.
Demerits
(a) This method can give only a linear trend of the data irrespective of whether it exists
or not.
(b) This is only a crude method of measuring trend, since we do not know whether the
effects of other components is completely eliminated or not.
3. Method of Moving Average: This method is based on the principle that the total effect of
periodic variations at different points of time in its cycle gets completely neutralised, i.e.,
S = 0 in one year and C = 0 in the period of cyclical variations.
t t
In the method of moving average, successive arithmetic averages are computed from
overlapping groups of successive values of a time series. Each group includes all the
observations in a given time interval, termed as the period of moving average. The next
group is obtained by replacing the oldest value by the next value in the series. The averages
of such groups are known as the moving averages.
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 229