Page 230 - DCAP402_DCAO204_DATABASE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM_MANAGING DATABASE
P. 230
Unit 13: Parallel Databases
Notes
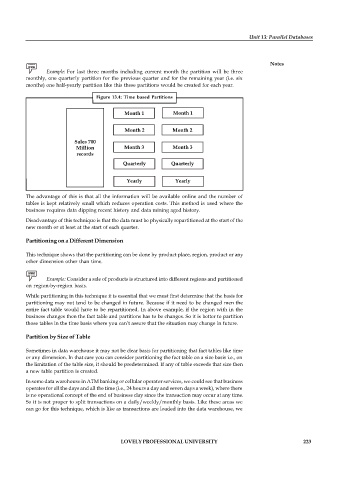
Example: For last three months including current month the partition will be three
monthly, one quarterly partition for the previous quarter and for the remaining year (i.e. six
months) one half-yearly partition like this these partitions would be created for each year.
Figure 13.4: Time based Partitions
Month 1 Month 1
Month 2 Month 2
Sales 700
Million Month 3 Month 3
records
Quarterly Quarterly
Yearly Yearly
The advantage of this is that all the information will be available online and the number of
tables is kept relatively small which reduces operation costs. This method is used where the
business requires data dipping recent history and data mining aged history.
Disadvantage of this technique is that the data must be physically repartitioned at the start of the
new month or at least at the start of each quarter.
Partitioning on a Different Dimension
This technique shows that the partitioning can be done by product place, region, product or any
other dimension other than time.
Example: Consider a sale of products is structured into different regions and partitioned
on region-by-region basis.
While partitioning in this technique it is essential that we must first determine that the basis for
partitioning may not tend to be changed in future. Because if it need to be changed men the
entire fact table would have to be repartitioned. In above example, if the region with in the
business changes then the fact table and partitions has to be changes. So it is better to partition
those tables in the time basis where you can’t assure that the situation may change in future.
Partition by Size of Table
Sometimes in data warehouse it may not be clear basis for partitioning that fact tables like time
or any dimension. In that case you can consider partitioning the fact table on a size basis i.e., on
the limitation of the table size, it should be predetermined. If any of table exceeds that size then
a new table partition is created.
In some data warehouse in ATM banking or cellular operator services, we could see that business
operates for all the days and all the time (i.e., 24 hours a day and seven days a week), where there
is no operational concept of the end of business clay since the transaction may occur at any time.
So it is not proper to split transactions on a daily/weekly/monthly basis. Like these areas we
can go for this technique, which is like as transactions are loaded into the data warehouse, we
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 223