Page 235 - DCAP402_DCAO204_DATABASE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM_MANAGING DATABASE
P. 235
Database Management Systems/Managing Database
Notes
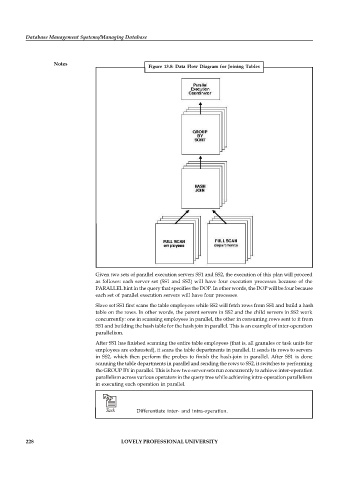
Figure 13.8: Data Flow Diagram for Joining Tables
Given two sets of parallel execution servers SS1 and SS2, the execution of this plan will proceed
as follows: each server set (SS1 and SS2) will have four execution processes because of the
PARALLEL hint in the query that specifies the DOP. In other words, the DOP will be four because
each set of parallel execution servers will have four processes.
Slave set SS1 first scans the table employees while SS2 will fetch rows from SS1 and build a hash
table on the rows. In other words, the parent servers in SS2 and the child servers in SS2 work
concurrently: one in scanning employees in parallel, the other in consuming rows sent to it from
SS1 and building the hash table for the hash join in parallel. This is an example of inter-operation
parallelism.
After SS1 has finished scanning the entire table employees (that is, all granules or task units for
employees are exhausted), it scans the table departments in parallel. It sends its rows to servers
in SS2, which then perform the probes to finish the hash-join in parallel. After SS1 is done
scanning the table departments in parallel and sending the rows to SS2, it switches to performing
the GROUP BY in parallel. This is how two server sets run concurrently to achieve inter-operation
parallelism across various operators in the query tree while achieving intra-operation parallelism
in executing each operation in parallel.
Task Differentiate inter- and intra-operation.
228 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY