Page 233 - DCAP402_DCAO204_DATABASE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM_MANAGING DATABASE
P. 233
Database Management Systems/Managing Database
Notes In Online Transaction Processing (OLTP) applications, each query is independent and takes a
relatively short time to execute. As the number of OLTP users increases, more queries are
generated. Without inter-query parallelism, all queries will be performed by a single processor
in a time-shared manner. This slows down response time. With inter-query parallelism, queries
generated by OLTP users can be distributed over multiple processors. Since the queries are
performed simultaneously by multiple processors, response time remains satisfactory.
13.4 Intra-query Parallelism
Intra-query parallelism is the ability to break a single query into subtasks and to execute those
subtasks in parallel using a different processor for each. The result is a decrease in the overall
elapsed time needed to execute a single query. Intra-query parallelism is very beneficial in
Decision Support System (DSS) applications, which often have complex, long-running queries.
As DSS systems have become more widely used, database vendors have been increasing their
support for intra-query parallelism.
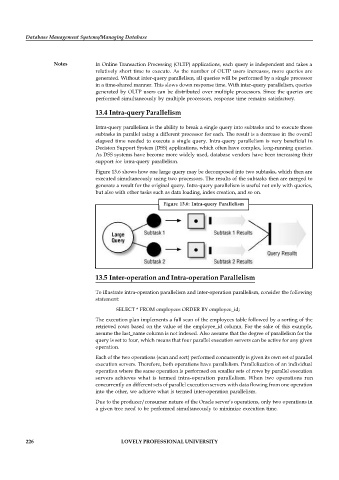
Figure 13.6 shows how one large query may be decomposed into two subtasks, which then are
executed simultaneously using two processors. The results of the subtasks then are merged to
generate a result for the original query. Intra-query parallelism is useful not only with queries,
but also with other tasks such as data loading, index creation, and so on.
Figure 13.6: Intra-query Parallelism
13.5 Inter-operation and Intra-operation Parallelism
To illustrate intra-operation parallelism and inter-operation parallelism, consider the following
statement:
SELECT * FROM employees ORDER BY employee_id;
The execution plan implements a full scan of the employees table followed by a sorting of the
retrieved rows based on the value of the employee_id column. For the sake of this example,
assume the last_name column is not indexed. Also assume that the degree of parallelism for the
query is set to four, which means that four parallel execution servers can be active for any given
operation.
Each of the two operations (scan and sort) performed concurrently is given its own set of parallel
execution servers. Therefore, both operations have parallelism. Parallelization of an individual
operation where the same operation is performed on smaller sets of rows by parallel execution
servers achieves what is termed intra-operation parallelism. When two operations run
concurrently on different sets of parallel execution servers with data flowing from one operation
into the other, we achieve what is termed inter-operation parallelism.
Due to the producer/consumer nature of the Oracle server’s operations, only two operations in
a given tree need to be performed simultaneously to minimize execution time.
226 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY