Page 71 - DCAP207_NETWORKS_DCAP406_COMPUTER_NETWORKS
P. 71
Computer Networks/Networks
Notes Address Table
As explained above, each bridge should have an address table that indicates the location of
different computers or nodes on the segments of LAN. More specifically, it indicates the connection
between nodes and ports. When a bridge is booted first time, this table is found to be blank.
Now this question arises how this table is filled with appropriate addresses of different nodes
attached to ports. Most of the bridges are called adaptive or self-leaning bridges because they
learn the location of the node and associated port themselves and make a list of nodes attached
each segment.
When a bridge receives a data packet from a computer, it first copies the physical address of that
computer contained in the packet into its list. Afterward, bridge determines whether this packet
should be forwarded or not. In other words, the bridge learns the location of the computer on
the network as soon as the computer on the network sends some packet.
If a computer does not send a packet, the bridge will never be able to determine its position and
unnecessarily forwards the packet on network. Fortunately, this cannot happen because a
computer with network software attached to a network transmits at least one frame when the
system first boots. Furthermore, computer communication is bi-directional, there is always an
acknowledgement for each received packets.
5.2.1 Bridge Protocols
Bridge protocols include spanning tree, source routing protocol, and source routing transparent.
Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) Bridge: This is also known as adaptive or self-learning bridges
and is defined in IEEE 802.1 standards. It has already been explained in the above section.
Ideally, in bridged network, the network tree of the bridge provides only one span (link) for
each LAN-to-LAN connection and therefore no network with bridges can form a loop. Sometimes
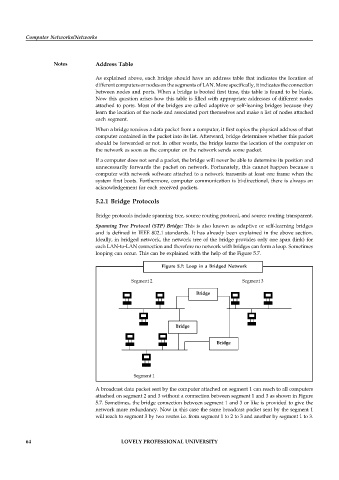
looping can occur. This can be explained with the help of the Figure 5.7.
Figure 5.7: Loop in a Bridged Network
Segment 2 Segment 3
Bridge
Bridge
Bridge
Segment 1
A broadcast data packet sent by the computer attached on segment 1 can reach to all computers
attached on segment 2 and 3 without a connection between segment 1 and 3 as shown in Figure
5.7. Sometimes, the bridge connection between segment 1 and 3 or like is provided to give the
network more redundancy. Now in this case the same broadcast packet sent by the segment 1
will reach to segment 3 by two routes i.e. from segment 1 to 2 to 3 and another by segment 1 to 3.
64 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY