Page 72 - DCAP207_NETWORKS_DCAP406_COMPUTER_NETWORKS
P. 72
Unit 5: Networking Devices
In this manner the computers on segment 3 will receive duplicate packets. In case of large Notes
networks some segments may receive many packets and thus causing looping.
A loop, therefore, can cause a broadcast packet or a packet with an unknown destination to
circulate through it, thus rendering the network inoperable. This condition is avoided by making
some bridges not to forward frames. An algorithm known as Distributed Spanning Tree (DST)
accomplishes this task. This algorithm decides which bridge should forward the packets in the
network. Under this scheme bridges exchange a control message known as a hello message to
select a single transmission route. Remaining bridges maintain a standby position and provide
alternate path in case of the some bridge fails in the selected transmission path. In Figure 5.8
bridge connecting segment 1 and 3 will be active only if the bridge connecting segment 2 and 3
fails otherwise it acts as a standby bridge for network. In other words, bridges that support the
spanning tree algorithm have the ability to automatically reconfigure themselves for alternate
paths if a network segment fails, thereby improving overall reliability.
IBM Source Routing Protocol (SRP) Bridge: These are programmed with specific routes for each
packet based on considerations such as the physical location of the nodes, and the number of
bridges involved.
Source Routing Transparent (SRT): It is defined in the IEEE 802.1 standard. It is effectively a
combination of STP and SRP. The SRT router can connect LANs by either method, as programmed.
5.2.2 Classification of Bridges
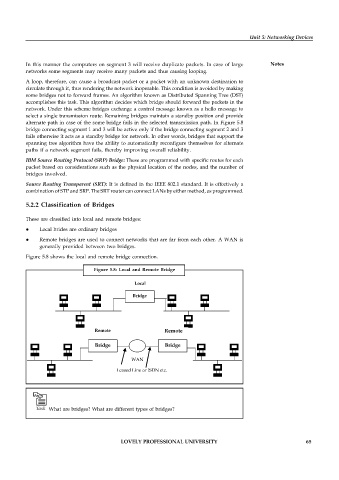
These are classified into local and remote bridges:
Local brides are ordinary bridges
Remote bridges are used to connect networks that are far from each other. A WAN is
generally provided between two bridges.
Figure 5.8 shows the local and remote bridge connection.
Figure 5.8: Local and Remote Bridge
Local
Bridge
Remote Remote
Bridge Bridge
WAN
Leased Line or ISDN etc.
Task What are bridges? What are different types of bridges?
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 65