Page 73 - DCAP207_NETWORKS_DCAP406_COMPUTER_NETWORKS
P. 73
Computer Networks/Networks
Notes 5.3 Gateways
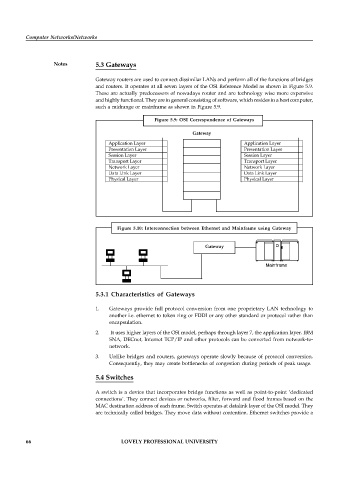
Gateway routers are used to connect dissimilar LANs and perform all of the functions of bridges
and routers. It operates at all seven layers of the OSI Reference Model as shown in Figure 5.9.
These are actually predecessors of nowadays router and are technology wise more expensive
and highly functional. They are in general consisting of software, which resides in a host computer,
such a midrange or mainframe as shown in Figure 5.9.
Figure 5.9: OSI Correspondence of Gateways
Gateway
Application Layer Application Layer
Presentation Layer Presentation Layer
Session Layer Session Layer
Transport Layer Transport Layer
Network Layer Network Layer
Data Link Layer Data Link Layer
Physical Layer Physical Layer
Figure 5.10: Interconnection between Ethernet and Mainframe using Gateway
Gateway
5.3.1 Characteristics of Gateways
1. Gateways provide full protocol conversion from one proprietary LAN technology to
another i.e. ethernet to token ring or FDDI or any other standard or protocol rather than
encapsulation.
2. It uses higher layers of the OSI model, perhaps through layer 7, the application layer. IBM
SNA, DECnet, Internet TCP/IP and other protocols can be converted from network-to-
network.
3. Unlike bridges and routers, gateways operate slowly because of protocol conversion.
Consequently, they may create bottlenecks of congestion during periods of peak usage.
5.4 Switches
A switch is a device that incorporates bridge functions as well as point-to-point ‘dedicated
connections’. They connect devices or networks, filter, forward and flood frames based on the
MAC destination address of each frame. Switch operates at datalink layer of the OSI model. They
are technically called bridges. They move data without contention. Ethernet switches provide a
66 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY