Page 13 - DMGT206_PRODUCTION_AND_OPERATIONS_MANAGEMENT
P. 13
Production and Operations Management
Notes 1.2.2 Transformation Approach
The traditional definition considers Operations Management to be a transformation system.
According to this view:
Operations Management is the business function that manages that part of a business that
transforms raw materials and human inputs into goods and services of higher value.
According to this definition, Operations Management transforms inputs into outputs of goods
or services.
Example: A manufacturing plant takes raw materials in the form of parts, components,
and subassemblies and transforms them into a manufactured product such as an automobile, by
the use of resources such as labour, capital, and energy.
It is the task of Operations Management to set-up and run the system that can produce or provide
the required outputs. The specifications of the outputs are the starting point. For getting the
desired output, the specifications and quality of the inputs is first determined. The responsibility
of Operations Management is to transform these inputs into outputs in such a way that the
outputs have greater value than the costs of inputs plus the costs related to investments in the
process.
This is because, in a system based on the input-output concept, controls can be basically exercised
on variable costs. The variable costs are made up of the input costs and the
process costs. Once a process has been selected, it is difficult to alter the processes; therefore,
process costs are relatively stable. The input costs reflect that part of variable costs that can
basically be controlled. Control of input costs, therefore, becomes the basis for the measurement
of performance of the system.
Did u know? The primary system of analysis and control of the effectiveness of the
Operations Management system is the breakeven analysis.
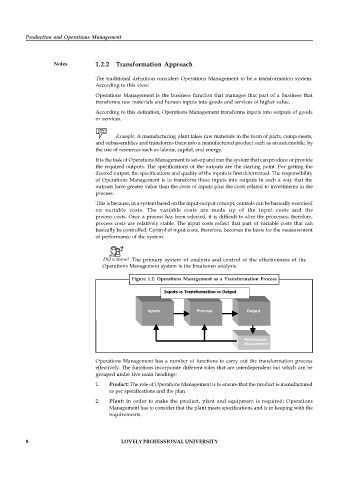
Figure 1.2: Operations Management as a Transformation Process
Inputs Transformation Output
Inputs Process Output
Performance
Measurement
Operations Management has a number of functions to carry out the transformation process
effectively. The functions incorporate different roles that are interdependent but which can be
grouped under five main headings:
1. Product: The role of Operations Management is to ensure that the product is manufactured
as per specifications and the plan.
2. Plant: In order to make the product, plant and equipment is required; Operations
Management has to consider that the plant meets specifications and is in keeping with the
requirements.
8 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY