Page 112 - DECO401_MICROECONOMIC_THEORY_ENGLISH
P. 112
Unit-6: Theory of Demand and Elasticity of Demand
Quantity demanded can be of two types: Notes
(i) Extension of demand—Extension of demand refers to a size in the demanded as a result of fall
in price. As shown in table 3, when rate of apples is 5 per Kg then demand of apple is 1 Kg and
when price decreases to 1 per Kg the demanded expanded to new demand of 5 Kg apples.
Table 3: Extension of Demand
Quantity
Price ( ) Description
Demanded (Kg)
5 1 Rise in price
↓
1 5 Extension in demand
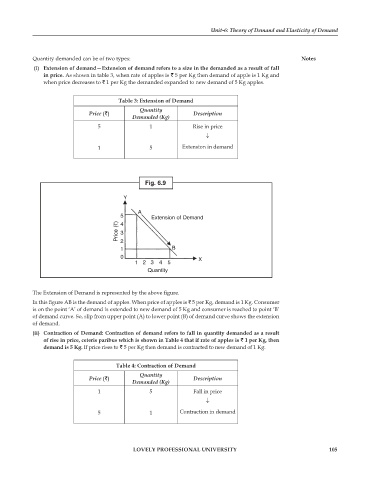
Fig. 6.9
Y
A
5 Extension of Demand
Price (`) 4
3
2
1 B
0 X
12 3 4 5
Quantity
The Extension of Demand is represented by the above figure.
In this figure AB is the demand of apples. When price of apples is 5 per Kg, demand is 1 Kg. Consumer
is on the point ‘A’ of demand is extended to new demand of 5 Kg and consumer is reached to point ‘B’
of demand curve. So, slip from upper point (A) to lower point (B) of demand curve shows the extension
of demand.
(ii) Contraction of Demand: Contraction of demand refers to fall in quantity demanded as a result
of rise in price, ceteris paribus which is shown in Table 4 that if rate of apples is 1 per Kg, then
demand is 5 Kg. If price rises to 5 per Kg then demand is contracted to new demand of 1 Kg.
Table 4: Contraction of Demand
Quantity
Price ( ) Description
Demanded (Kg)
1 5 Fall in price
↓
5 1 Contraction in demand
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 105