Page 113 - DECO401_MICROECONOMIC_THEORY_ENGLISH
P. 113
Microeconomic Theory
Notes
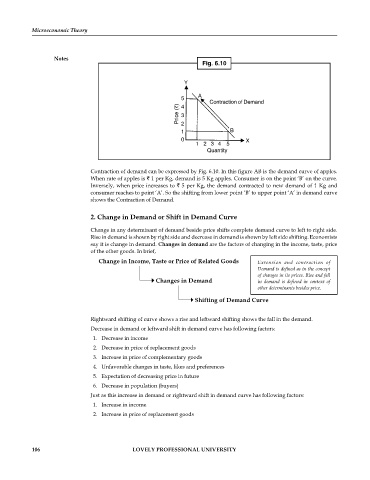
Fig. 6.10
Y
A
5
Contraction of Demand
Price (`) 3
4
2
1 B
0 X
1 234 5
Quantity
Contraction of demand can be expressed by Fig. 6.10. In this figure AB is the demand curve of apples.
When rate of apples is 1 per Kg, demand is 5 Kg apples. Consumer is on the point ‘B’ on the curve.
Inversely, when price increases to 5 per Kg, the demand contracted to new demand of 1 Kg and
consumer reaches to point ‘A’. So the shifting from lower point ‘B’ to upper point ‘A’ in demand curve
shows the Contraction of Demand.
2. Change in Demand or Shift in Demand Curve
Change in any determinant of demand beside price shifts complete demand curve to left to right side.
Rise in demand is shown by right side and decrease in demand is shown by left side shifting. Economists
say it is change in demand. Changes in demand are the factors of changing in the income, taste, price
of the other goods. In brief,
Change in Income, Taste or Price of Related Goods Extension and contraction of
Demand is defined as in the concept
of changes in its prices. Rise and fall
Changes in Demand in demand is defined in context of
other determinants besides price.
Shifting of Demand Curve
Rightward shifting of curve shows a rise and leftward shifting shows the fall in the demand.
Decrease in demand or leftward shift in demand curve has following factors:
1. Decrease in income
2. Decrease in price of replacement goods
3. Increase in price of complementary goods
4. Unfavorable changes in taste, likes and preferences
5. Expectation of decreasing price in future
6. Decrease in population (buyers)
Just as this increase in demand or rightward shift in demand curve has following factors:
1. Increase in income
2. Increase in price of replacement goods
106 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY