Page 118 - DECO401_MICROECONOMIC_THEORY_ENGLISH
P. 118
Unit-6: Theory of Demand and Elasticity of Demand
Notes
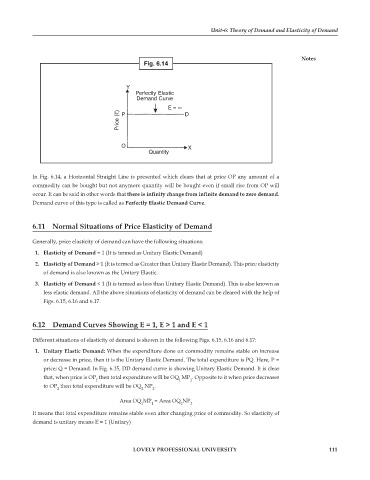
Fig. 6.14
Y
Perfectly Elastic
Demand Curve
E = ∞
Price (`) P D
O X
Quantity
In Fig. 6.14, a Horizontal Straight Line is presented which clears that at price OP any amount of a
commodity can be bought but not anymore quantity will be bought even if small rise from OP will
occur. It can be said in other words that there is infinity change from infinite demand to zero demand.
Demand curve of this type is called as Perfectly Elastic Demand Curve.
6.11 Normal Situations of Price Elasticity of Demand
Generally, price elasticity of demand can have the following situations:
1. Elasticity of Demand = 1 (It is termed as Unitary Elastic Demand)
2. Elasticity of Demand > 1 (It is termed as Greater than Unitary Elastic Demand). This price elasticity
of demand is also known as the Unitary Elastic.
3. Elasticity of Demand < 1 (It is termed as less than Unitary Elastic Demand). This is also known as
less elastic demand. All the above situations of elasticity of demand can be cleared with the help of
Figs. 6.15, 6.16 and 6.17.
6.12 Demand Curves Showing E = 1, E > 1 and E < 1
Different situations of elasticity of demand is shown in the following Figs. 6.15, 6.16 and 6.17:
1. Unitary Elastic Demand: When the expenditure done on commodity remains stable on increase
or decrease in price, then it is the Unitary Elastic Demand. The total expenditure is PQ. Here, P =
price; Q = Demand. In Fig. 6.15, DD demand curve is showing Unitary Elastic Demand. It is clear
that, when price is OP then total expenditure will be OQ MP . Opposite to it when price decreases
1 1 1
to OP then total expenditure will be OQ NP .
2
2
2
Area OQ MP = Area OQ NP
1 1 2 2
It means that total expenditure remains stable even after changing price of commodity. So elasticity of
demand is unitary means E = 1 (Unitary)
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 111