Page 132 - DECO401_MICROECONOMIC_THEORY_ENGLISH
P. 132
Unit-6: Theory of Demand and Elasticity of Demand
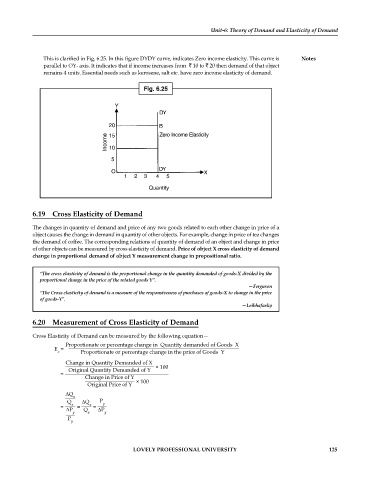
This is clarified in Fig. 6.25. In this figure DYDY curve, indicates Zero income elasticity. This curve is Notes
parallel to OY- axis. It indicates that if income increases from 10 to 20 then demand of that object
remains 4 units. Essential needs such as kerosene, salt etc. have zero income elasticity of demand.
Fig. 6.25
Y
DY
20 B
Income 15 Zero Income Elasticity
10
5
DY
O X
1 2 3 4 5
Quantity
6.19 Cross Elasticity of Demand
The changes in quantity of demand and price of any two goods related to each other change in price of a
object causes the change in demand in quantity of other objects. For example, change in price of tea changes
the demand of coffee. The corresponding relations of quantity of demand of an object and change in price
of other objects can be measured by cross elasticity of demand. Price of object X cross elasticity of demand
change in proportional demand of object Y measurement change in propositional ratio.
“The cross elasticity of demand is the proportional change in the quantity demanded of goods-X divided by the
proportional change in the price of the related goods Y”.
—Ferguson
“The Cross elasticity of demand is a measure of the responsiveness of purchases of goods-X to change in the price
of goods-Y”.
—Leibhafasky
6.20 Measurement of Cross Elasticity of Demand
Cross Elasticity of Demand can be measured by the following equation—
Proportionate or percentage change in Quantity demanded of Goods X
E = _______________________________________________________________
c Proportionate or percentage change in the price of Goods Y
Change in Quantity Demanded of X
_________________________________
× 100
Original Quantity Demanded of Y
= _______________________________________
Change in Price of Y
___________________ × 100
Original Price of Y
∆Q
____ x P
Q
____
y
x
= ____ = ∆Q x = ____
∆P Q ∆P
____ y x y
P
y
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 125