Page 130 - DECO401_MICROECONOMIC_THEORY_ENGLISH
P. 130
Unit-6: Theory of Demand and Elasticity of Demand
∆Q Notes
___
Q
___
___
Y __
Y __
E = ____ = ∆Q × = × ∆Q
y ∆Y ∆Y Q Q ∆Y
___
Y
∆Q
Y __
E = × ___
y Q ∆Y
Here E = Income Elasticity of Demand; Q = Initial Income; Y = Initial Income; ∆Q = Changes in the
y
Volume of Demand; ∆Y = Changes in Income.
Illustration
When your monthly income (Y) is 300 then you buy 10 ice creams (Q), if your monthly income (Y )
1
increases to 600 then your demand increases to 30 ice creams. Find income Elasticity of Demand of
Ice creams.
Solution:
Income Elasticity of Demand can be measured by the help of following equation:
∆Q
Y __
E = × ___
y Q ∆Y
Here Y= 300 ; Y 600; ∆Y = Y – Y = 600 – 300 = 300; Q = 10 Units of Ice cream ; Q = 30 Units of
1
1
1
Ice cream; ∆Q = Q – Q = 30 Units – 10 Units = 20 Units of Ice cream
1
300
20
E = ____ × ____ = 2 (more than unity)
y 10 300
6.18 Degrees of Income Elasticity of Demand
There are three types of income Elasticity of Demand:
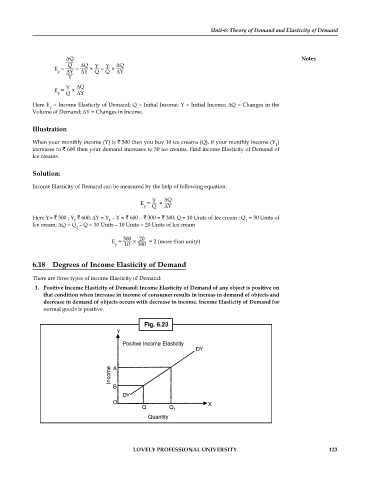
1. Positive Income Elasticity of Demand: Income Elasticity of Demand of any object is positive on
that condition when increase in income of consumer results in increas in demand of objects and
decrease in demand of objects occurs with decrease in income. Income Elasticity of Demand for
normal goods is positive.
Fig. 6.23
Y
Positive Income Elasticity
DY
Income A
B
DY
O X
Q Q
1
Quantity
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 123