Page 131 - DECO401_MICROECONOMIC_THEORY_ENGLISH
P. 131
Microeconomic Theory
Notes It can be described with the help of Fig. 6.23. Quality of
demands of an object is shown on OX-axis and income Income elasticity of demand of normal objects
of consumer is shown on OY-axis. Curve DYDY shows is positive while object of below normal
positive income elasticity of demand. Slope of this curve is income elasticity of demand is negative.
inclined from left to right which indicates that on increasing
income demand increases and decreases on decreasing income.
There can be three kind of positive income elasticity of demand—
(i) Unitary Income Elasticity of Demand: Positive income elasticity of demand is unitary on that
situation when changes in percentage of income, same percentage changes in the quantity
of demand. Suppose that if income increases in percentage and also 100 percentage increase in
demand then
100%
E = _____ = 1 units (Unitary)
y 100%
(ii) Less than Unitary Income Elasticity of Demand or Income Inelastic Demand: The less unitary
income elasticity of demand happens when the percentage changes in demand is less than
percentage changes in income. If income raises by 100% but demand increase by only 50 and
then
50%
1 __
E = _____ = Less than units (Less than unitary)
y 100% 2
(iii) More than Unitary Income Elasticity of Demand or Income Elastic Demand: This happens
when the percentage changes in demand is greater than percentage changes in income. For
example, if income rises by 100% and demand raises by 200% then
_____
E = 200% = more than 2 units (Greater than Unitary)
y 100%
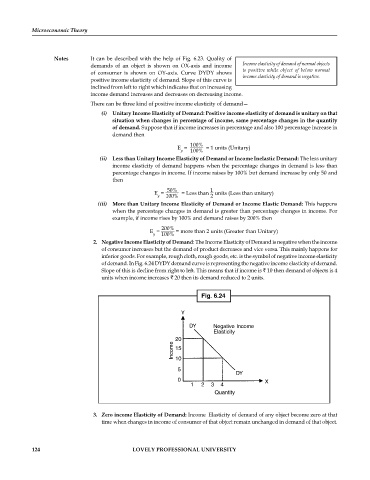
2. Negative Income Elasticity of Demand: The Income Elasticity of Demand is negative when the income
of consumer increases but the demand of product decreases and vice versa. This mainly happens for
inferior goods. For example, rough cloth, rough goods, etc. is the symbol of negative income elasticity
of demand. In Fig. 6.24 DYDY demand curve is representing the negative income elasticity of demand.
Slope of this is decline from right to left. This means that if income is 10 then demand of objects is 4
units when income increases 20 then its demand reduced to 2 units.
Fig. 6.24
Y
DY Negative Income
Elasticity
20
Income 15
10
5
DY
0 X
1 2 3 4
Quantity
3. Zero income Elasticity of Demand: Income Elasticity of demand of any object become zero at that
time when changes in income of consumer of that object remain unchanged in demand of that object.
124 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY