Page 126 - DECO401_MICROECONOMIC_THEORY_ENGLISH
P. 126
Unit-6: Theory of Demand and Elasticity of Demand
a factory is also known as demand curve. The elasticity of demand by Average revenue and Marginal Notes
A
, (Here, E = Price elasticity of demand,
revenue can be determined by the following formula— E = ______ d
A – M
d
A = Average Revenue; M = Marginal Revenue).
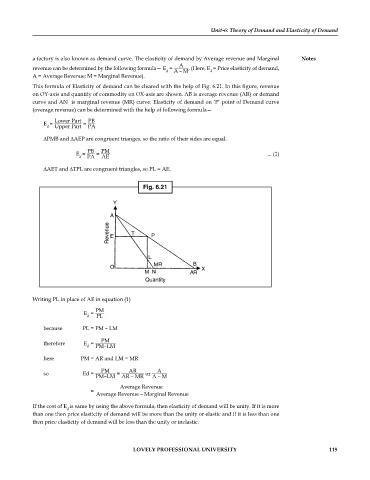
This formula of Elasticity of demand can be cleared with the help of Fig. 6.21. In this figure, revenue
on OY-axis and quantity of commodity on OX-axis are shown. AB is average revenue (AR) or demand
curve and AN is marginal revenue (MR) curve. Elasticity of demand on ‘P’ point of Demand curve
(average revenue) can be determined with the help of following formula—
Lower Part ___
PB
___________
E = = PA
d Upper Part
∆PMB and ∆AEP are congruent trianges, so the ratio of their sides are equal.
PM
PB
E = ___ = ____ ... (1)
d PA
AE
∆AET and ∆TPL are congruent triangles, so PL = AE.
Fig. 6.21
Y
A
Revenue E T P
L
MR B
O X
MN AR
Quantity
Writing PL in place of AE in equation (1)
____
E = PM
PL
d
because PL = PM – LM
PM
therefore E = ________
PM–LM
d
here PM = AR and LM = MR
AR
A
PM
so Ed = ________ = _________ or ______
PM–LM AR – MR A – M
Average Revenue
= __________________________________
Average Revenue – Marginal Revenue
If the cost of E is same by using the above formula, then elasticity of demand will be unity. If it is more
d
than one then price elasticity of demand will be more than the unity or elastic and if it is less than one
then price elasticity of demand will be less than the unity or inelastic.
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 119