Page 21 - DECO401_MICROECONOMIC_THEORY_ENGLISH
P. 21
Microeconomic Theory
Notes
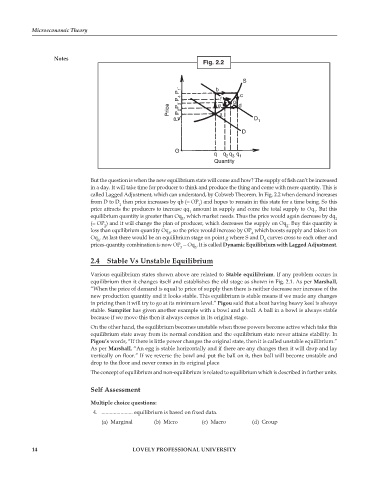
Fig. 2.2
S
P 1 b
P 4 f g c
Price P 3 P 2 e a d
P D 1
D
O
q q q q
2 3 1
Quantity
But the question is when the new equilibrium state will come and how? The supply of fish can’t be increased
in a day. It will take time for producer to think and produce the thing and come with more quantity. This is
called Lagged Adjustment, which can understand, by Cobweb Theorem. In Fig. 2.2 when demand increases
from D to D then price increases by qb (= OP ) and hopes to remain in this state for a time being. So this
1
1
price attracts the producers to increase qq amount in supply and come the total supply to Oq . But this
1
1
equilibrium quantity is greater than Oq , which market needs. Thus the price would again decrease by dq
1
3
(= OP ) and it will change the plan of producer, which decreases the supply on Oq . Buy this quantity is
2
2
less than equilibrium quantity Oq , so the price would increase by OP which boosts supply and takes it on
4
3
Oq . At last there would be an equilibrium stage on point g where S and D curves cross to each other and
1
3
prices-quantity combination is now OP - Oq . It is called Dynamic Equilibrium with Lagged Adjustment.
3
3
2.4 Stable Vs Unstable Equilibrium
Various equilibrium states shown above are related to Stable equilibrium. If any problem occurs in
equilibrium then it changes itself and establishes the old stage as shown in Fig. 2.1. As per Marshall,
“When the price of demand is equal to price of supply then there is neither decrease nor increase of the
new production quantity and it looks stable. This equilibrium is stable means if we made any changes
in pricing then it will try to go at its minimum level.” Pigou said that a boat having heavy keel is always
stable. Sumpiter has given another example with a bowl and a ball. A ball in a bowl is always stable
because if we move this then it always comes in its original stage.
On the other hand, the equilibrium becomes unstable when those powers become active which take this
equilibrium state away from its normal condition and the equilibrium state never attains stability. In
Pigou’s words, “If there is little power changes the original state, then it is called unstable equilibrium.”
As per Marshall, “An egg is stable horizontally and if there are any changes then it will drop and lay
vertically on floor.” If we reverse the bowl and put the ball on it, then ball will become unstable and
drop to the floor and never comes in its original place
The concept of equilibrium and non-equilibrium is related to equilibrium which is described in further units.
Self Assessment
Multiple choice questions:
4. ....................... equilibrium is based on fixed data.
(a) Marginal (b) Micro (c) Macro (d) Group
14 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY