Page 26 - DECO401_MICROECONOMIC_THEORY_ENGLISH
P. 26
Unit-2: The Concept of Equilibrium
As the equilibrium of demand and supply, the factor-service and supply needs to be equal for General Notes
Equilibrium. The service demand comes from producers and supply comes from consumers. If the
technique is given and the profit target has given, then the production cost of a product depends
upon the production cost of various products produces by that producer. Since the economy has
full employment so the market is stable for the factors; when the service for product is equal to the
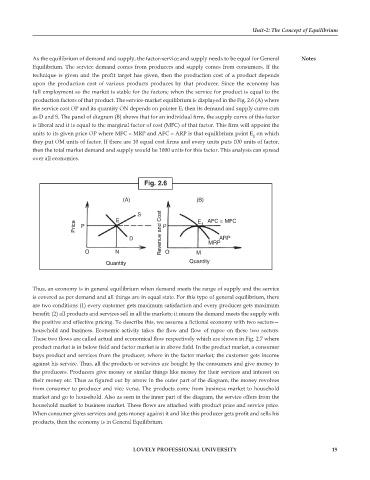
production factors of that product. The service-market equilibrium is displayed in the Fig. 2.6 (A) where
the service cost OP and its quantity ON depends on pointer E, then its demand and supply curve cuts
as D and S. The panel of diagram (B) shows that for an individual firm, the supply curve of this factor
is liberal and it is equal to the marginal factor of cost (MFC) of that factor. This firm will appoint the
units to its given price OP where MFC = MRP and AFC = ARP is that equilibrium point E on which
1
they put OM units of factor. If there are 10 equal cost firms and every units puts 100 units of factor,
then the total market demand and supply would be 1000 units for this factor. This analysis can spread
over all economies.
Fig. 2.6
(A) (B)
S
Price P E P E 1 AFC = MFC
D Revenue and Cost MRP ARP
O N O M
Quantity Quantity
Thus, an economy is in general equilibrium when demand meets the range of supply and the service
is covered as per demand and all things are in equal state. For this type of general equilibrium, there
are two conditions (1) every customer gets maximum satisfaction and every producer gets maximum
benefit; (2) all products and services sell in all the markets; it means the demand meets the supply with
the positive and effective pricing. To describe this, we assume a fictional economy with two sectors—
household and business. Economic activity takes the flow and flow of rupee on these two sectors.
These two flows are called actual and economical flow respectively which are shown in Fig. 2.7 where
product market is in below field and factor market is in above field. In the product market, a consumer
buys product and services from the producer, where in the factor market; the customer gets income
against his service. Thus, all the products or services are bought by the consumers and give money to
the producers. Producers give money or similar things like money for their services and interest on
their money etc. Thus as figured out by arrow in the outer part of the diagram, the money revolves
from consumer to producer and vice versa. The products come from business market to household
market and go to household. Also as seen in the inner part of the diagram, the service offers from the
household market to business market. These flows are attached with product price and service price.
When consumer gives services and gets money against it and like this producer gets profit and sells his
products, then the economy is in General Equilibrium.
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 19