Page 22 - DECO401_MICROECONOMIC_THEORY_ENGLISH
P. 22
Unit-2: The Concept of Equilibrium
5. The marginal analysis has ....................... types of economical problem. Notes
(a) four (b) two (c) one (d) three
6. Every firm of industry sells its things on ....................... price.
(a) initial (b) lateral (c) current (d) marginal
7. Marginal analysis has its own ...................... .
(a) habits (b) laws (c) region (d) boundary
8. The measurement of result is ...................... .
(a) unstable (b) stable (c) small (d) large
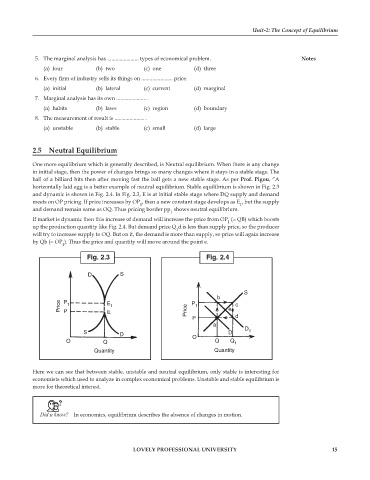
2.5 Neutral Equilibrium
One more equilibrium which is generally described, is Neutral equilibrium. When there is any change
in initial stage, then the power of changes brings so many changes where it stays in a stable stage. The
ball of a billiard hits then after moving fast the ball gets a new stable stage. As per Prof. Pigou, “A
horizontally laid egg is a better example of neutral equilibrium. Stable equilibrium is shown in Fig. 2.3
and dynamic is shown in Fig. 2.4. In Fig. 2.3, E is at initial stable stage where DQ supply and demand
meets on OP pricing. If price increases by OP , then a new constant stage develops as E , but the supply
1
1
and demand remain same as OQ. Thus pricing border pp shows neutral equilibrium.
1
If market is dynamic then this increase of demand will increase the price from OP (= QB) which boosts
1
up the production quantity like Fig. 2.4. But demand price Q d is less than supply price, so the producer
1
will try to increase supply to OQ. But on it, the demand is more than supply, so price will again increase
by Qb (= OP ). Thus the price and quantity will move around the point e.
1
Fig. 2.3 Fig. 2.4
D S
S
b
Price P 1 E 1 Price P 1 e c
P
E
P d
a
D
S D 1
D O
O Q Q Q 1
Quantity Quantity
Here we can see that between stable, unstable and neutral equilibrium, only stable is interesting for
economists which used to analyze in complex economical problems. Unstable and stable equilibrium is
more for theoretical interest.
In economics, equilibrium describes the absence of changes in motion.
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 15