Page 218 - DECO401_MICROECONOMIC_THEORY_ENGLISH
P. 218
Unit-10: Isoquant Curve
(Here ∆K = Changes in capital, ∆L = Changes in labour, MP = Marginal product of labour, MP = Marginal Notes
L
K
product of capital, P = Labour costs, P = Cost of capital, MRTS = Marginal rate of technical substitution
L
LK
K
of labour and capital)
10.11 Principle of Substitution
According to principle of substitution, the process of production changes by changing the factors of
production. Relatively, cheaper factor is substituted for the other factor or more of the relatively
cheaper factor is used and less of the other.
The pricing affects more to the production factors and distribution of factors in production process.
Illustration: Let’s assume a producer wants to produce 100 pens. Also assume that in equilibrium
state (by satisfying the law of minimum cost or profit maximization) 10 units of capital and 15 units of
labour are used. Total expenditure is 1500 if the price is 75 per unit for capital and 50 per unit for
labour.
This can be represented as—
Production Inputs Price Total expenditure (in )
Q K L P P L
K
100 10 15 75 50 750 + 750 = 1,500
Now assume that the cost of labour (P ) is increased from 50 to 75. So to produce the similar rate
L
(with constant combination of inputs), the status would change as following—
Production Inputs Price Total expenditure (in )
Q K L P P
K L
100 10 15 75 75 750 + 1125 = 1,875
Thus if there is no change in inputs, then the cost of production increases from 1500 to 1875 while
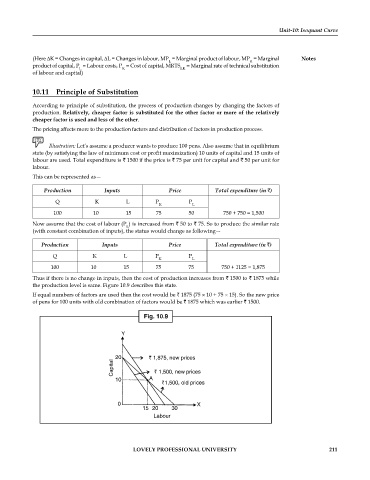
the production level is same. Figure 10.9 describes this state.
If equal numbers of factors are used then the cost would be ` 1875 (75 × 10 + 75 × 15). So the new price
of pens for 100 units with old combination of factors would be ` 1875 which was earlier ` 1500.
Fig. 10.9
Y
20 ` 1,875, new prices
Capital ` 1,500, new prices
10 A
` 1,500, old prices
0 X
15 20 30
Labour
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 211