Page 220 - DECO401_MICROECONOMIC_THEORY_ENGLISH
P. 220
Unit-10: Isoquant Curve
Notes
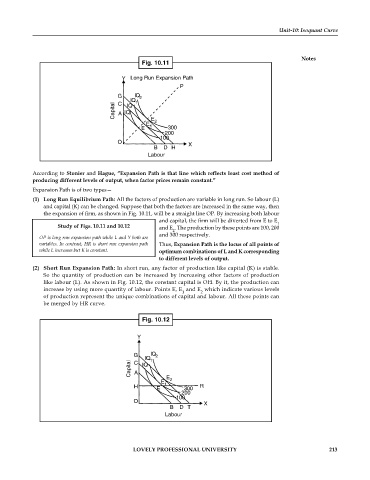
Fig. 10.11
Y Long Run Expansion Path
P
G IQ 2
IQ 1
C
Capital A IQ
IQ
E 1 E 2
E 300
200
100
O X
B D H
Labour
According to Stonier and Hague, “Expansion Path is that line which reflects least cost method of
producing different levels of output, when factor prices remain constant.”
Expansion Path is of two types—
(1) Long Run Equilibrium Path: All the factors of production are variable in long run. So labour (L)
and capital (K) can be changed. Suppose that both the factors are increased in the same way, then
the expansion of firm, as shown in Fig. 10.11, will be a straight line OP. By increasing both labour
and capital, the firm will be diverted from E to E
1
Study of Figs. 10.11 and 10.12 and E . The production by these points are 100, 200
2
and 300 respectively.
OP is long run expansion path while L and Y both are
variables. In contrast, HR is short run expansion path Thus, Expansion Path is the locus of all points of
while L increases but K is constant. optimum combinations of L and K corresponding
to different levels of output.
(2) Short Run Expansion Path: In short run, any factor of production like capital (K) is stable.
So the quantity of production can be increased by increasing other factors of production
like labour (L). As shown in Fig. 10.12, the constant capital is OH. By it, the production can
increase by using more quantity of labour. Points E, E and E which indicate various levels
2
1
of production represent the unique combinations of capital and labour. All these points can
be merged by HR curve.
Fig. 10.12
Y
G IQ 2
IQ 1
Capital A IQ
C
E 1 E 2
H E 300 R
200
100
O X
B D T
Labour
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 213