Page 247 - DECO401_MICROECONOMIC_THEORY_ENGLISH
P. 247
Microeconomic Theory
Notes 7. Fall in cash preference results in reserve price being
(a) less (b) more (c) unreserved (d) none of these
8. If seller hopes that costs will increase in future, then they will fix reserve price .................... .
(a) less (b) very high (c) high (d) none of these
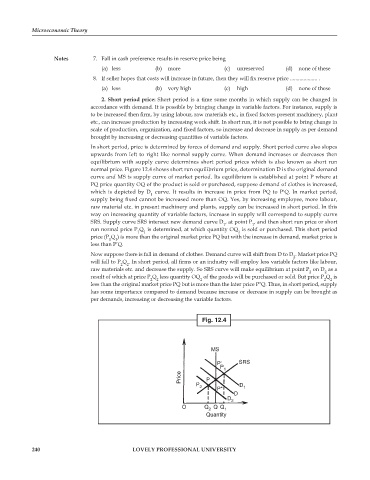
2. Short period price: Short period is a time some months in which supply can be changed in
accordance with demand. It is possible by bringing change in variable factors. For instance, supply is
to be increased then firm, by using labour, raw materials etc., in fixed factors present machinery, plant
etc., can increase production by increasing work shift. In short run, it is not possible to bring change in
scale of production, organization, and fixed factors, so increase and decrease in supply as per demand
brought by increasing or decreasing quantities of variable factors.
In short period, price is determined by forces of demand and supply. Short period curve also slopes
upwards from left to right like normal supply curve. When demand increases or decreases then
equilibrium with supply curve determines short period prices which is also known as short run
normal price. Figure 12.4 shows short run equilibrium price, determination D is the original demand
curve and MS is supply curve of market period. Its equilibrium is established at point P where at
PQ price quantity OQ of the product is sold or purchased, suppose demand of clothes is increased,
which is depicted by D curve. It results in increase in price from PQ to P'Q. In market period,
1
supply being fixed cannot be increased more than OQ. Yes, by increasing employee, more labour,
raw material etc. in present machinery and plants, supply can be increased in short period. In this
way on increasing quantity of variable factors, increase in supply will correspond to supply curve
SRS. Supply curve SRS intersect new demand curve D , at point P , and then short run price or short
1
1
run normal price P Q is determined, at which quantity OQ is sold or purchased. This short period
1
1
1
price (P Q ) is more than the original market price PQ but with the increase in demand, market price is
1
1
less than P’Q.
Now suppose there is fall in demand of clothes. Demand curve will shift from D to D . Market price PQ
2
will fall to P Q . In short period, all firms or an industry will employ less variable factors like labour,
2
2
raw materials etc. and decrease the supply. So SRS curve will make equilibrium at point P on D as a
2
2
result of which at price P Q less quantity OQ of the goods will be purchased or sold. But price P Q is
2
2
2
2
2
less than the original market price PQ but is more than the later price P"Q. Thus, in short period, supply
has some importance compared to demand because increase or decrease in supply can be brought as
per demands, increasing or decreasing the variable factors.
Fig. 12.4
MS
P' SRS
P
1
Price P
P D
2 1
P"
D
D
2
O Q QQ
2 1
Quantity
240 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY