Page 248 - DECO401_MICROECONOMIC_THEORY_ENGLISH
P. 248
Unit-12: Pricing Under Perfect Competition
3. Long period price or Normal Price: Long period is of many years in which supply can be Notes
adjusted in accordance with demand. In the long run, supply can be changed corresponding to demand
buying changes in the fixed factors. It is that time in which old machines, equipment, plants etc. can be
replaced with the new machines, equipment etc. New firms can enter into the industry and old firms
can leave the industry. Scale of production, organization and management of firms can be changed. So
in long run, supply can be adjusted as per demand from every point of view.
Long run price is also known as normal price. Normal price is that price which has the possibility to
exist in the long run, and which is fixed in the long run. In the words of Marshall, “Normal or natural
value is that which economic forces would tend to bring about in the long run.” Actually, normal
price is the price between very high price and very low price which has the possibility to exist in the
long run. It is that price around which all other prices revolve.
Long run or normal price is determined by the equilibrium of demand and supply. In long run, it is
necessary for firms and industry that normal price of the goods would be equal to marginal cost and
average cost. If price would be higher than the minimum average cost then every firm will earn Super
Normal Profits which will attract new firm to enter into the industry, then supply will increase and
price will be reduced and will be equal to minimum average cost. On the other hand, firm will incur
losses when prices will be less than the average costs. Some firms which could not incur the losses will
leave the industry, then supply will be reduced and price will rise to be equal to average cost. Thus, long
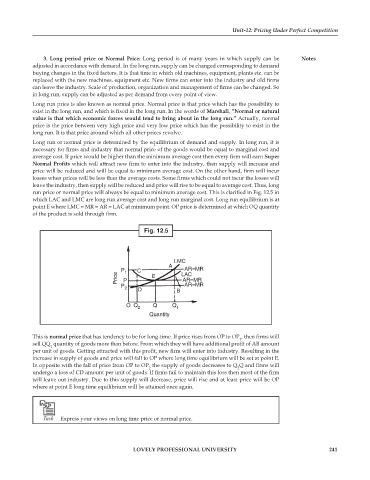
run price or normal price will always be equal to minimum average cost. This is clarified in Fig. 12.5 in
which LAC and LMC are long run average cost and long run marginal cost. Long run equilibrium is at
point E where LMC = MR = AR = LAC at minimum point. OP price is determined at which OQ quantity
of the product is sold through firm.
Fig. 12.5
LMC
A AR=MR
Price P P 1 E LAC
C
AR=MR
P AR=MR
2 D B
OQ Q Q
2 1
Quantity
This is normal price that has tendency to be for long-time. If price rises from OP to OP , then firms will
1
sell QQ quantity of goods more than before. From which they will have additional profit of AB amount
1
per unit of goods. Getting attracted with this profit, new firm will enter into industry. Resulting in the
increase in supply of goods and price will fall to OP where long time equilibrium will be set at point E.
In opposite with the fall of price from OP to OP the supply of goods decreases to Q Q and firms will
2
2
undergo a loss of CD amount per unit of goods. If firms fail to maintain this loss then most of the firm
will leave out industry. Due to this supply will decrease, price will rise and at least price will be OP
where at point E long time equilibrium will be attained once again.
Express your views on long time price or normal price.
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 241