Page 249 - DECO401_MICROECONOMIC_THEORY_ENGLISH
P. 249
Microeconomic Theory
Notes Long-Run Price and the Laws of Returns: In the analysis of Long-Run Price, it is important to understand
when this price will be more, less or equal to market price that means what affects laws of return put on
long-run price. If industry produces according to the law of decreasing return or increasing cost, then
long-run price will be more than original market price. When law of constant return or constant cost
applies, then the long-run price will be equal to original market price, whereas on the application of law
of increasing return or decreasing cost, long-run price will be less than original market price. Long-run
price determination on increase in demand under various production laws is explained below with the
help of Fig. 12.6.
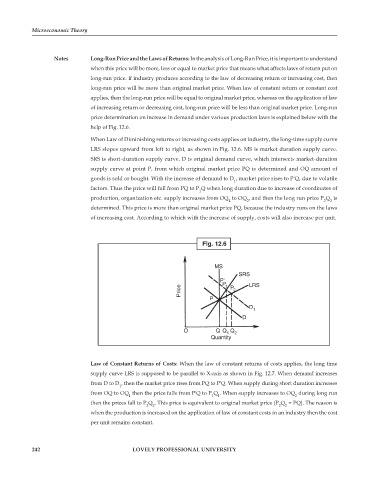
When Law of Diminishing returns or increasing costs applies on industry, the long-time supply curve
LRS slopes upward from left to right, as shown in Fig. 12.6. MS is market duration supply curve.
SRS is short-duration supply curve. D is original demand curve, which intersects market-duration
supply curve at point P, from which original market price PQ is determined and OQ amount of
goods is sold or bought. With the increase of demand to D , market price rises to P'Q, due to volatile
1
factors. Thus the price will fall from PQ to P Q when long duration due to increase of coordinates of
1
production, organization etc. supply increases from OQ to OQ , and then the long run price P Q is
2
1
2
2
determined. This price is more than original market price PQ, because the industry runs on the laws
of increasing cost. According to which with the increase of supply, costs will also increase per unit.
Fig. 12.6
MS
SRS
P' P LRS
Price 1 P 2
P
D
1
D
O Q Q Q
1 2
Quantity
Law of Constant Returns of Costs: When the law of constant returns of costs applies, the long time
supply curve LRS is supposed to be parallel to X-axis as shown in Fig. 12.7. When demand increases
from D to D , then the market price rises from PQ to P'Q. When supply during short duration increases
1
from OQ to OQ then the price falls from P'Q to P Q . When supply increases to OQ during long run
1 1 1 2
then the prices fall to P Q . This price is equivalent to original market price (P Q = PQ). The reason is
2
2
2
2
when the production is increased on the application of law of constant costs in an industry then the cost
per unit remains constant.
242 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY