Page 278 - DECO401_MICROECONOMIC_THEORY_ENGLISH
P. 278
Unit-14: Theory of Monopolistic Competition
b
Notes
Fig. 14.4
Y
Normal Profit
LAC
LMC
Revenue\Cost
A
P
E
MC = MR AR
MR
O X
M
Output
Self Assessment
Multiple choice questions:
5. Intension of every producer even in monopolistic competition is to be .................. .
(a) more (b) less (c) zero (d) none of these
6. There .................. of entry and exit of firms in the situation of monopolistic competition.
(a) dependence (b) freedom (c) equality (d) inequality
7. It is found in firms in monopolistic competition .................. .
(a) freedom (b) equality (c) excess capacity (d) dependence
8. Under cost competition, firms do to cost .................. .
(a) more (b) zero (c) less (d) none of these
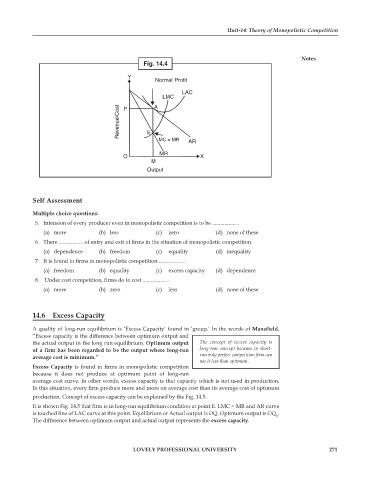
14.6 Excess Capacity
A quality of long-run equilibrium is ‘Excess Capacity’ found in ‘group.’ In the words of Mansfield,
“Excess capacity is the difference between optimum output and
the actual output in the long run equilibrium. Optimum output The concept of excess capacity is
of a firm has been regarded to be the output where long-run long-run concept because in short-
average cost is minimum.” run only perfect competition firm can
use it less than optimum.
Excess Capacity is found in firms in monopolistic competition
because it does not produce at optimum point of long-run
average cost curve. In other words, excess capacity is that capacity which is not used in production.
In this situation, every firm produce more and more on average cost than its average cost of optimum
production. Concept of excess capacity can be explained by the Fig. 14.5.
It is shown Fig. 14.5 that firm is in long-run equilibrium condition at point E. LMC = MR and AR curve
is touched line of LAC curve at this point. Equilibrium or Actual output is OQ. Optimum output is OQ .
1
The difference between optimum output and actual output represents the excess capacity.
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 271