Page 275 - DECO401_MICROECONOMIC_THEORY_ENGLISH
P. 275
Microeconomic Theory
Notes Average Revenue Curve(AR Curve) and Marginal Revenue (MR Curve) fall down in the form of left to
right. In monopolistic competition, a firm produce till the point or limit at which (i) Marginal Revenue
is equal to Marginal Cost (MR = MC) and (ii) Marginal Revenue Curve cuts Marginal Cost Curve from
the lower side. In this situation firm is in the condition of balancing by the production. The study of
equilibrium firm in monopolistic competition can be done in two different durations—
(1) Short Run and (2) Long Run
Monopolistic Competition is that situation of market in which there are many sellers of
the commodity but commodity of every seller is different from commodities of other
sellers in any form.
14.4 Short Run Equilibrium in Monopolistic Competition
Short Run is that duration of time in which production can be increased only by increase in using
variable resources on increasing demand. There is no time to increase or decrease constant resources
of production like machine, plant, building, etc. In short run, an equilibrium of a firm will be in that
situation in which (1) MC = MR and (2) MC curve will be cutting MR curve. In short run, the amount of
profit obtained in situation of equilibrium production
to the firm will depend on demand of commodity The similarity of the MR and MC-
and work welfare. There can be three conditions of balance is the standard condition
firms in this duration of time—
Standard condition of similar equilibrium of MR
(1) Super Normal Profits, (2) Normal Profits and and MC is in the condition of maximum profit and
(3) Minimum Losses. Short minimum term minimum loss of monopoly and perfect competition
equilibrium condition of firm of monopolistic in monopolistic competition is also MR = MC
competition can be explained by the leading figure.
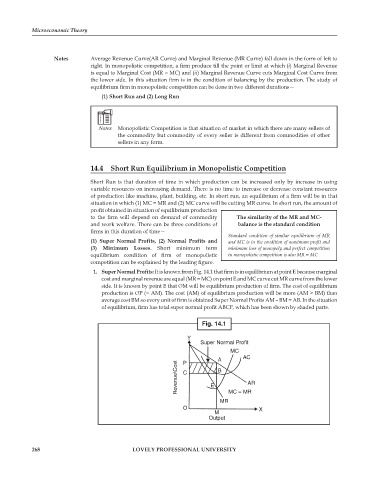
1. Super Normal Profits: It is known from Fig. 14.1 that firm is in equilibrium at point E because marginal
cost and marginal revenue are equal (MR = MC) on point E and MC curve cut MR curve from the lower
side. It is known by point E that OM will be equilibrium production of firm. The cost of equilibrium
production is OP (= AM). The cost (AM) of equilibrium production will be more (AM > BM) than
average cost BM so every unit of firm is obtained Super Normal Profits AM – BM = AB. In the situation
of equilibrium, firm has total super normal profit ABCP, which has been shown by shaded parts.
Fig. 14.1
Y
Super Normal Profit
MC
AC
A
P
Revenue\Cost C E B AR
MR MC = MR
O X
M
Output
268 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY