Page 276 - DECO401_MICROECONOMIC_THEORY_ENGLISH
P. 276
Unit-14: Theory of Monopolistic Competition
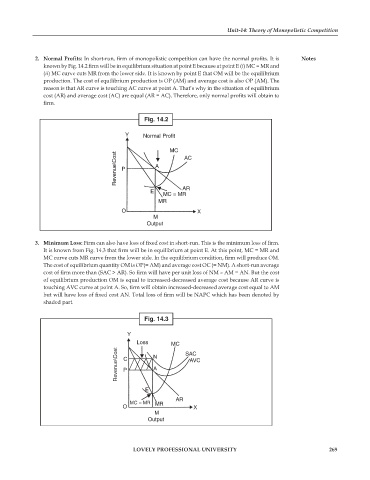
2. Normal Profits: In short-run, firm of monopolistic competition can have the normal profits. It is Notes
known by Fig. 14.2 firm will be in equilibrium situation at point E because at point E (i) MC = MR and
(ii) MC curve cuts MR from the lower side. It is known by point E that OM will be the equilibrium
production. The cost of equilibrium production is OP (AM) and average cost is also OP (AM). The
reason is that AR curve is touching AC curve at point A. That’s why in the situation of equilibrium
cost (AR) and average cost (AC) are equal (AR = AC). Therefore, only normal profits will obtain to
firm.
Fig. 14.2
Y Normal Profit
MC AC
Revenue\Cost P A
AR
E
MC = MR
MR
O X
M
Output
3. Minimum Loss: Firm can also have loss of fixed cost in short-run. This is the minimum loss of firm.
It is known from Fig. 14.3 that firm will be in equilibrium at point E. At this point, MC = MR and
MC curve cuts MR curve from the lower side. In the equilibrium condition, firm will produce OM.
The cost of equilibrium quantity OM is OP(= AM) and average cost OC (= NM). A short-run average
cost of firm more than (SAC > AR). So firm will have per unit loss of NM – AM = AN. But the cost
of equilibrium production OM is equal to increased-decreased average cost because AR curve is
touching AVC curve at point A. So, firm will obtain increased-decreased average cost equal to AM
but will have loss of fixed cost AN. Total loss of firm will be NAPC which has been denoted by
shaded part.
Fig. 14.3
Y
Loss MC
Revenue\Cost C N SAC
AVC
A
P
E
AR
MC = MR MR
O X
M
Output
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 269