Page 270 - DECO401_MICROECONOMIC_THEORY_ENGLISH
P. 270
Unit-13: Theory of Monopoly Firm
13.18 Supply Curve of a Firm Under Monopoly Notes
In perfect competition that part of marginal cost curve which lies above the average variable cost curve,
is short run supply curve of the firm because at a price less than the average variable cost the firm cannot
realize even its variable cost and it shuts down its production.
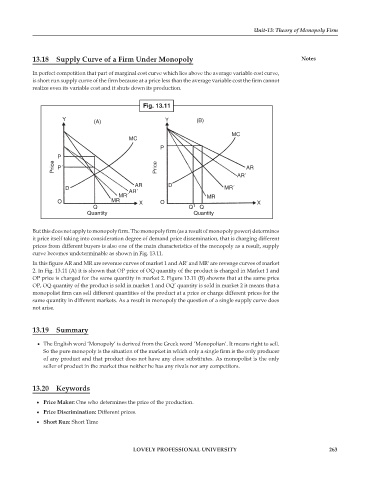
Fig. 13.11
Y Y
(A) (B)
MC
MC
P
P
Price P' Price AR
AR'
AR D
D AR' MR'
MR' MR
O MR X O X
Q Q 1 Q
Quantity Quantity
But this does not apply to monopoly firm. The monopoly firm (as a result of monopoly power) determines
it price itself taking into consideration degree of demand price dissemination, that is charging different
prices from different buyers is also one of the main characteristics of the monopoly as a result, supply
curve becomes undeterminable as shown in Fig. 13.11.
In this figure AR and MR are revenue curves of market 1 and AR′ and MR′ are revenge curves of market
2. In Fig. 13.11 (A) it is shown that OP price of OQ quantity of the product is charged in Market 1 and
OP price is charged for the same quantity in market 2. Figure 13.11 (B) showns that at the same price
OP, OQ quantity of the product is sold in market 1 and OQ’ quantity is sold in market 2 it means that a
monopolist firm can sell different quantities of the product at a price or charge different prices for the
same quantity in different markets. As a result in monopoly the question of a single supply curve does
not arise.
13.19 Summary
· The English word ‘Monopoly’ is derived from the Greek word ‘Monopolian’. It means right to sell.
So the pure monopoly is the situation of the market in which only a single firm is the only producer
of any product and that product does not have any close substitutes. As monopolist is the only
seller of product in the market thus neither he has any rivals nor any competitors.
13.20 Keywords
· Price Maker: One who determines the price of the production.
· Price Discrimination: Different prices.
· Short Run: Short Time
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 263