Page 266 - DECO401_MICROECONOMIC_THEORY_ENGLISH
P. 266
Unit-13: Theory of Monopoly Firm
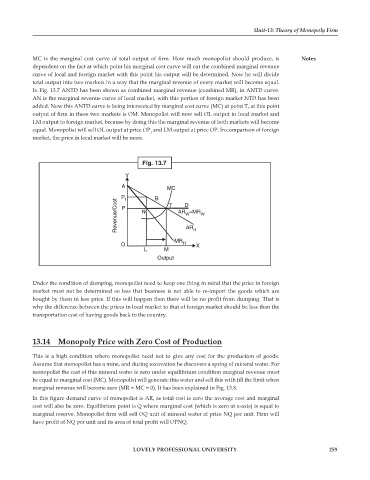
MC is the marginal cost curve of total output of firm. How much monopolist should produce, is Notes
dependent on the fact at which point his marginal cost curve will cut the combined marginal revenue
curve of local and foreign market with this point his output will be determined. Now he will divide
total output into two markets in a way that the marginal revenue of every market will become equal.
In Fig. 13.7 ANTD has been shown as combined marginal revenue (combined MR), in ANTD curve.
AN is the marginal revenue curve of local market, with this portion of foreign market NTD has been
added. Now this ANTD curve is being intersected by marginal cost curve (MC) at point T, at this point
output of firm in these two markets is OM. Monopolist will now sell OL output in local market and
LM output to foreign market, because by doing this the marginal revenue of both markets will become
equal. Monopolist will sell OL output at price OP and LM output at price OP. In comparison of foreign
1
market, the price in local market will be more.
Fig. 13.7
Y
A MC
P 1 B T D
Revenue/Cost P N AR =MR W
W
AR
MR H
O H X
L M
Output
Under the condition of dumping, monopolist need to keep one thing in mind that the price in foreign
market must not be determined so less that business is not able to re-import the goods which are
bought by them in less price. If this will happen then there will be no profit from dumping. That is
why the difference between the prices in local market to that of foreign market should be less than the
transportation cost of having goods back to the country.
13.14 Monopoly Price with Zero Cost of Production
This is a high condition where monopolist need not to give any cost for the production of goods.
Assume that monopolist has a mine, and during excavation he discovers a spring of mineral water. For
monopolist the cast of this mineral water is zero under equilibrium condition marginal revenue must
be equal to marginal cost (MC). Monopolist will generate this water and sell this with till the limit when
marginal revenue will become zero (MR = MC = 0). It has been explained in Fig. 13.8.
In this figure demand curve of monopolist is AR, as total cost is zero the average cost and marginal
cost will also be zero. Equilibrium point is Q where marginal cost (which is zero at x-axis) is equal to
marginal reserve. Monopolist firm will sell OQ unit of mineral water at price NQ per unit. Firm will
have profit of NQ per unit and its area of total profit will OPNQ.
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 259