Page 268 - DECO401_MICROECONOMIC_THEORY_ENGLISH
P. 268
Unit-13: Theory of Monopoly Firm
at marginal unit and if he produces from plant B then he will have to spend additional cost of 20 at Notes
marginal unit. In this way an increasing production at B and on reducing production at plant A there will
be shortage of marginal cost of 5, where the total production 9 the monopolist (Plant A’s production +
Plant B’s Production) remains fixed (150 + 100 = 250 units)
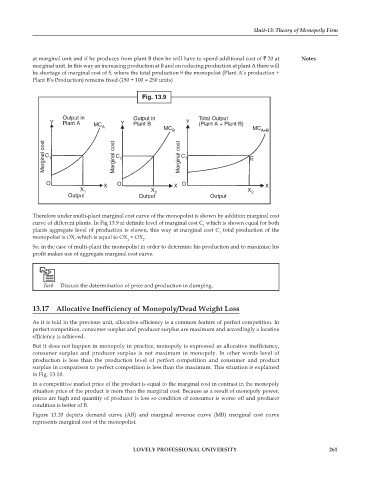
Fig. 13.9
Output in Output in Total Output
Y Plant A MC Y Plant B Y (Plant A + Plant B)
A MC MC
B A+B
Marginal cost C 1 Marginal cost C 1 Marginal cost C 1 E
O X O X O X
X X X
1 2 2
Output Output Output
Therefore under multi-plant marginal cost curve of the monopolist is shown by addition marginal cost
curve of different plants. In Fig 13.9 at definite level of marginal cost C which is shown equal for both
1
plants aggregate level of production is shown, this way at marginal cost C total production of the
1
monopolist is OX, which is equal to OX + OX .
1 2
So, in the case of multi-plant the monopolist in order to determine his production and to maximize his
profit makes use of aggregate marginal cost curve.
Discuss the determination of price and production in dumping.
13.17 Allocative Inefficiency of Monopoly/Dead Weight Loss
As it is told in the previous unit, allocative efficiency is a common feature of perfect competition. In
perfect competition, consumer surplus and producer surplus are maximum and accordingly a locative
efficiency is achieved.
But it does not happen in monopoly in practice, monopoly is expressed as allocative inefficiency,
consumer surplus and producer surplus is not maximum in monopoly. In other words level of
production is less than the production level of perfect competition and consumer and product
surplus in comparison to perfect competition is less than the maximum. This situation is explained
in Fig. 13.10.
In a competitive market price of the product is equal to the marginal cost in contrast in the monopoly
situation price of the product is more than the marginal cost. Because as a result of monopoly power,
prices are high and quantity of producer is less so condition of consumer is worse off and producer
condition is better of B.
Figure 13.10 depicts demand curve (AR) and marginal revenue curve (MR) marginal cost curve
represents marginal cost of the monopolist.
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 261