Page 269 - DECO401_MICROECONOMIC_THEORY_ENGLISH
P. 269
Microeconomic Theory
Notes
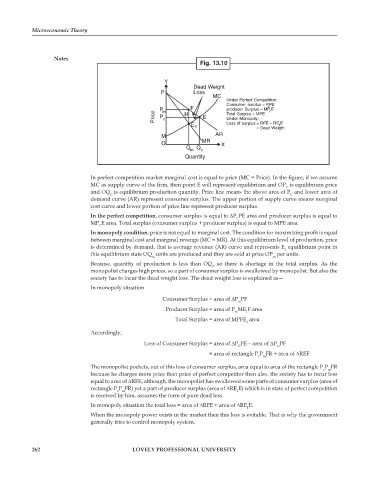
Fig. 13.10
Y
Dead Weight
P Loss
MC
Under Perfect Competition:
Consumer surplus = PPE
c
P m F producer Surplus = MP E
c
Price P c R E Total Surplus = MPE
Under Monopoly:
E Loss of surplus = RFE + RE E
1
1 = Dead Weight
M AR
MR
O X
Q Q
m c
Quantity
In perfect competition market marginal cost is equal to price (MC = Price). In the figure, if we assume
MC as supply curve of the firm, then point E will represent equilibrium and OP is equilibrium price
C
and OQ is equilibrium production quantity. Price line means the above area of P and lower area of
C
C
demand curve (AR) represent consumer surplus. The upper portion of supply curve means marginal
cost curve and lower portion of price line represent producer surplus.
In the perfect competition, consumer surplus is equal to ∆P PE area and producer surplus is equal to
C
MP E area. Total surplus (consumer surplus + producer surplus) is equal to MPE area.
C
In monopoly condition, price is not equal to marginal cost. The condition for maximizing profit is equal
between marginal cost and marginal revenge (MC = MR). At this equilibrium level of production, price
is determined by demand, that is average revenue (AR) curve and represents E equilibrium point in
1
this equilibrium state OQ units are produced and they are sold at price OP per units.
m m
Because, quantity of production is less than OQ , so there is shortage in the total surplus. As the
c
monopolist charges high prices, so a part of consumer surplus is swallowed by monopolist. But also the
society has to incur the dead weight loss. The dead weight loss is explained as —
In monopoly situation
Consumer Surplus = area of ∆P PF
m
Producer Surplus = area of P ME F area
m 1
Total Surplus = area of MPFE area
1
Accordingly,
Loss of Consumer Surplus = area of ∆P PE – area of ∆P PF
C
m
= area of rectangle P P FR + area of ∆REF
c m
The monopolist pockets, out of this loss of consumer surplus, area equal to area of the rectangle P P FR
m
c
because he charges more price than price of perfect competitor then also, the society has to incur loss
equal to area of ∆RFE, although, the monopolist has swallowed some parts of consumer surplus (area of
rectangle P P FR) yet a part of producer surplus (area of ∆RE E) which is in state of perfect competition
m
1
c
is received by him, assumes the form of pure dead loss.
In monopoly situation the total loss = area of ∆RFE + area of ∆RE E.
1
When the monopoly power exists in the market then this loss is evitable. That is why the government
generally tries to control monopoly system.
262 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY